双编码器可能是设置语义问答系统最有效的方式。这种架构依赖于同一个神经网络模型,该模型为问题和答案创建向量嵌入。其假设是,在潜在空间中,问题和答案的表示应该彼此接近。之所以如此,是因为它们都应该描述相同的语义概念。但这不适用于“是”或“否”之类的答案,但标准 FAQ 式问题会更容易一些,因为通常这两种文本之间存在重叠。不一定是在措辞上,而是在语义上。
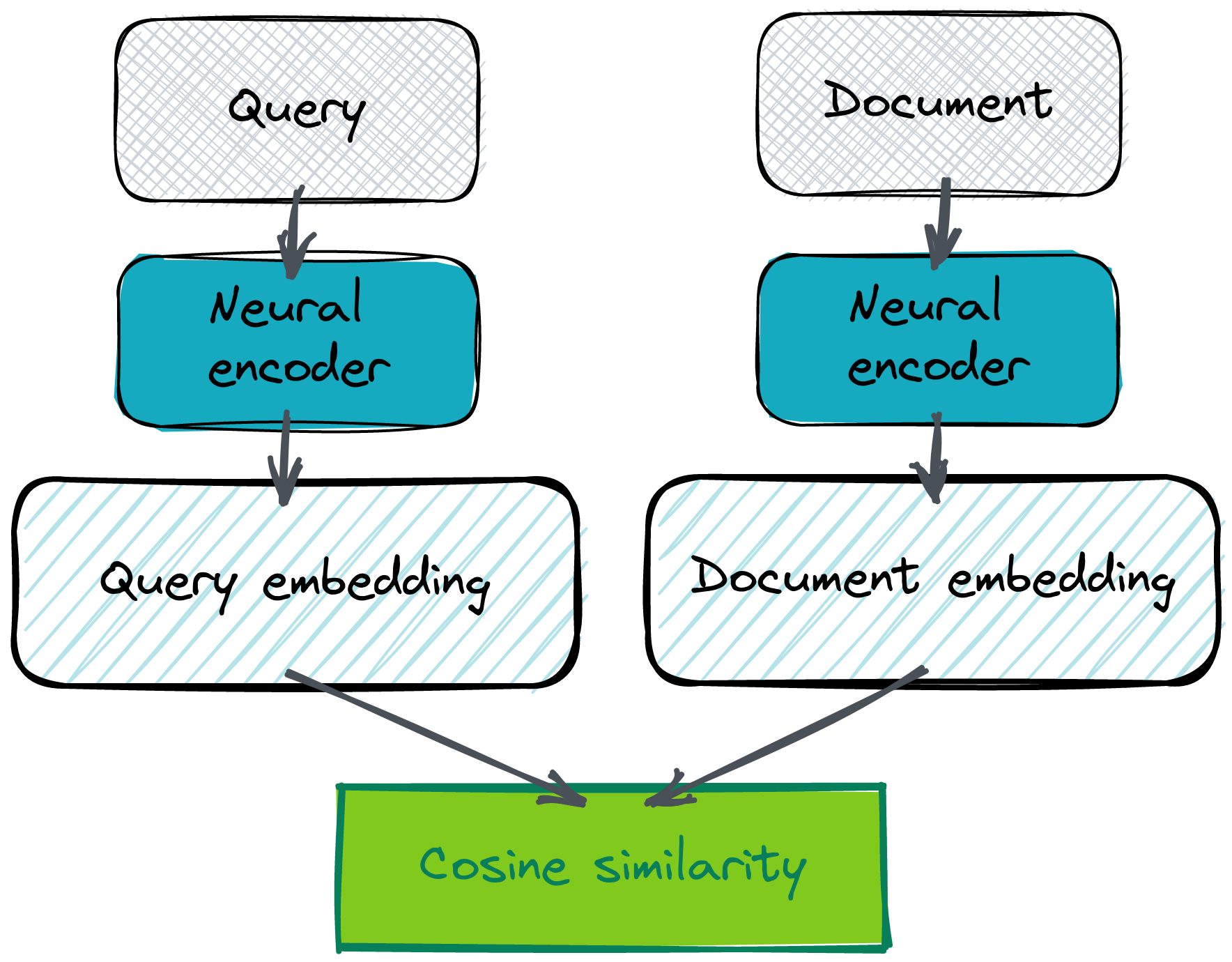
是的,你需要自带嵌入才能开始。获取嵌入有多种方法,但使用 Cohere co.embed API 可能是最简单便捷的方法。
为什么 co.embed API 和 Qdrant 配合得很好?
维护一个大型语言模型可能既困难又昂贵。当流量变化时,对其进行扩展和缩减需要更多的努力,并且变得不可预测。这对于任何语义搜索系统来说都可能是一个障碍。但是,如果你想立即开始,可以考虑使用 SaaS 模型,特别是 Cohere 的 co.embed API。它为你提供了最先进的语言模型,作为高度可用的 HTTP 服务,无需训练或维护自己的服务。由于所有通信都通过 JSON 完成,你可以简单地将 co.embed 输出作为 Qdrant 输入。
# Putting the co.embed API response directly as Qdrant method input
qdrant_client.upsert(
collection_name="collection",
points=rest.Batch(
ids=[...],
vectors=cohere_client.embed(...).embeddings,
payloads=[...],
),
)
这两个工具易于结合,因此你可以在几分钟内(而不是几天)开始使用语义搜索。
如果你的需求非常具体,需要对通用模型进行微调怎么办?Co.embed API 超越了预训练编码器,允许提供一些自定义数据集来使用你自己的数据自定义嵌入模型。因此,你可以在不担心基础设施的情况下获得领域特定模型的质量。
系统架构概述
在实际系统中,答案会被向量化并存储在高效的向量搜索数据库中。我们通常甚至不需要提供具体的答案,而只需使用文本的句子或段落并对其进行向量化。不过,如果一段稍长的文本包含特定问题的答案,它与问题嵌入的距离不应该太远。而且肯定比所有其他不匹配的答案更近。将答案嵌入存储在向量数据库中使搜索过程变得更容易。
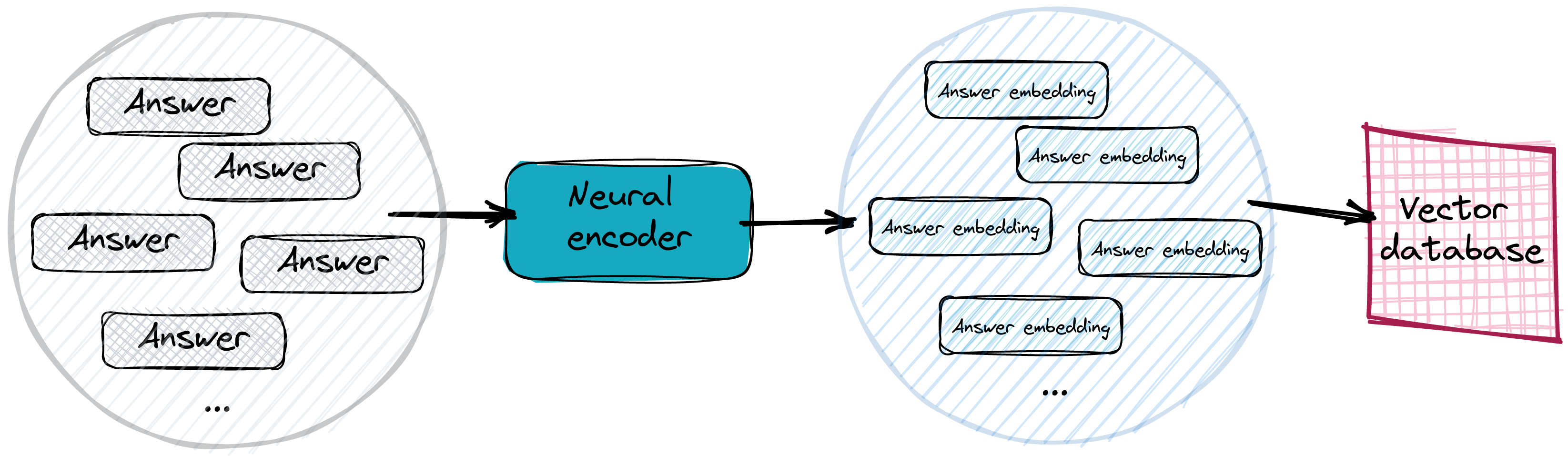
寻找正确答案
一旦我们的数据库正常工作且所有答案嵌入都已到位,我们就可以开始查询它了。我们基本上对给定问题执行相同的向量化操作,并要求数据库提供一些近邻。我们依赖于嵌入彼此接近,因此我们期望潜在空间中距离最小的点包含正确的答案。
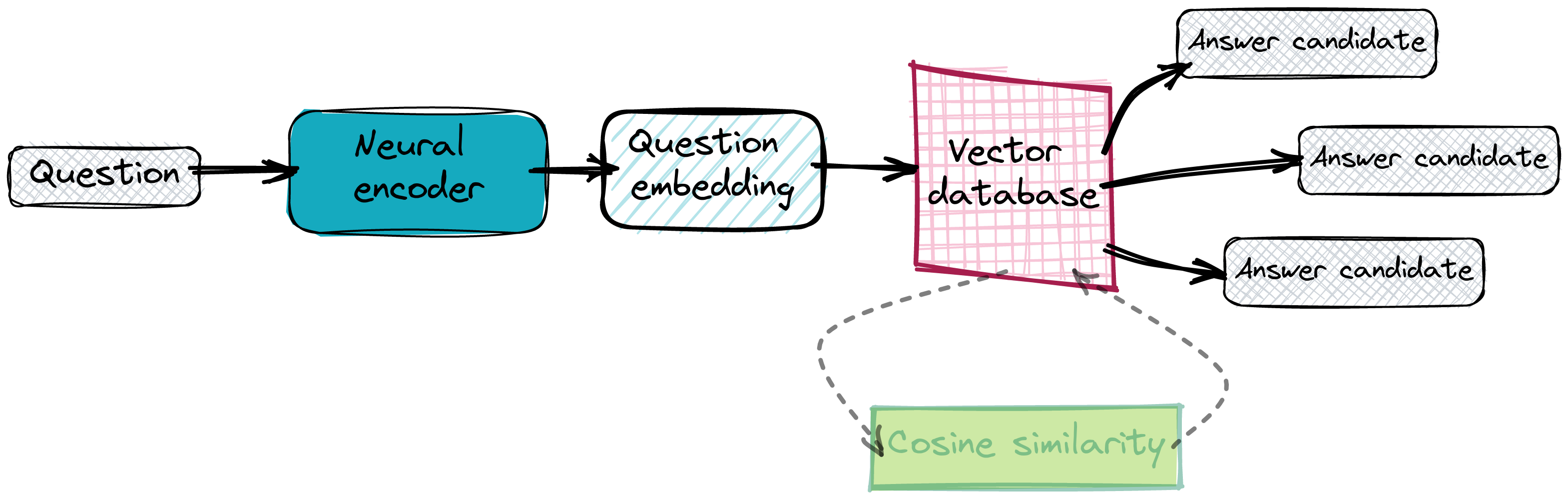
使用 SaaS 工具实现 QA 搜索系统
我们不想维护自己的神经网络编码器服务,甚至不想设置 Qdrant 实例。这两种情况都有 SaaS 解决方案——Cohere 的 co.embed API 和 Qdrant Cloud,所以我们将使用它们而不是本地工具。
生物医学数据上的问答
我们将为生物医学数据实现问答系统。有一个 pubmed_qa 数据集,其中 pqa_labeled 子集包含 1,000 个由领域专家标记的问题和答案示例。我们的系统将使用 co.embed API 生成的嵌入,并将其加载到 Qdrant。使用 Qdrant Cloud 与你自己的实例在此处差别不大。连接到云实例的方式存在细微差异,但所有其他操作都以相同的方式执行。
from datasets import load_dataset
# Loading the dataset from HuggingFace hub. It consists of several columns: pubid,
# question, context, long_answer and final_decision. For the purposes of our system,
# we’ll use question and long_answer.
dataset = load_dataset("pubmed_qa", "pqa_labeled")
| 出版物ID | 问题 | 上下文 | 长答案 | 最终决定 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18802997 | 钙卫蛋白能否预测炎症性肠病复发风险? | ... | 测量钙卫蛋白可能有助于识别 UC... | 可能 |
| 20538207 | 肾脏移植期间是否应监测体温? | ... | 新的存储方式可以提供更稳定的温度... | 否 |
| 25521278 | 盘子清空是肥胖的危险因素吗? | ... | 吃饭时清空盘子的倾向... | 是 |
| 17595200 | 是否存在宫内环境对肥胖的影响? | ... | 母子和父子比较... | 否 |
| 15280782 | 艾滋病感染者中不安全性行为是否增加? | ... | 没有证据表明不安全性行为有增加的趋势... | 否 |
使用 Cohere 和 Qdrant 构建答案数据库
为了开始生成嵌入,你需要创建一个 Cohere 账户。这将启动你的试用期,因此你将能够免费对文本进行向量化。登录后,你的默认 API 密钥将显示在设置中。我们将需要它来通过官方 python 包调用 co.embed API。
import cohere
cohere_client = cohere.Client(COHERE_API_KEY)
# Generating the embeddings with Cohere client library
embeddings = cohere_client.embed(
texts=["A test sentence"],
model="large",
)
vector_size = len(embeddings.embeddings[0])
print(vector_size) # output: 4096
让我们首先连接到 Qdrant 实例并创建一个具有适当配置的集合,以便我们以后可以将一些嵌入放入其中。
# Connecting to Qdrant Cloud with qdrant-client requires providing the api_key.
# If you use an on-premise instance, it has to be skipped.
qdrant_client = QdrantClient(
host="xyz-example.eu-central.aws.cloud.qdrant.io",
prefer_grpc=True,
api_key=QDRANT_API_KEY,
)
现在我们能够对所有答案进行向量化。它们将构成我们的集合,因此我们也可以将它们与有效负载和标识符一起放入 Qdrant。这将使我们的数据集易于搜索。
answer_response = cohere_client.embed(
texts=dataset["train"]["long_answer"],
model="large",
)
vectors = [
# Conversion to float is required for Qdrant
list(map(float, vector))
for vector in answer_response.embeddings
]
ids = [entry["pubid"] for entry in dataset["train"]]
# Filling up Qdrant collection with the embeddings generated by Cohere co.embed API
qdrant_client.upsert(
collection_name="pubmed_qa",
points=rest.Batch(
ids=ids,
vectors=vectors,
payloads=list(dataset["train"]),
)
)
就是这样。我们甚至没有设置自己的单个服务器,就创建了一个可以轻松提问的系统。我不想称之为无服务器,因为这个术语已经被使用了,但 co.embed API 与 Qdrant Cloud 使一切维护起来都更容易。
通过语义搜索回答问题 — 质量
是时候用一些问题来查询我们的数据库了。衡量系统整体质量可能很有趣。在这种类型的问题中,我们通常使用top-k 准确率。我们假设如果正确答案出现在前k个结果中,则系统的预测是正确的。
# Finding the position at which Qdrant provided the expected answer for each question.
# That allows to calculate accuracy@k for different values of k.
k_max = 10
answer_positions = []
for embedding, pubid in tqdm(zip(question_response.embeddings, ids)):
response = qdrant_client.search(
collection_name="pubmed_qa",
query_vector=embedding,
limit=k_max,
)
answer_ids = [record.id for record in response]
if pubid in answer_ids:
answer_positions.append(answer_ids.index(pubid))
else:
answer_positions.append(-1)
保存的答案位置允许我们计算不同k值的指标。
# Prepared answer positions are being used to calculate different values of accuracy@k
for k in range(1, k_max + 1):
correct_answers = len(
list(
filter(lambda x: 0 <= x < k, answer_positions)
)
)
print(f"accuracy@{k} =", correct_answers / len(dataset["train"]))
以下是不同 k 值对应的 top-k 准确率值
| 指标 | 值 |
|---|---|
| accuracy@1 | 0.877 |
| accuracy@2 | 0.921 |
| accuracy@3 | 0.942 |
| accuracy@4 | 0.950 |
| accuracy@5 | 0.956 |
| accuracy@6 | 0.960 |
| accuracy@7 | 0.964 |
| accuracy@8 | 0.971 |
| accuracy@9 | 0.976 |
| accuracy@10 | 0.977 |
看起来我们的系统即使只考虑距离最小的第一个结果,也运行得相当好。我们大约有 12% 的问题未能成功。但随着 k 值的增加,准确率也随之提高。检查我们的系统未能回答的问题,以及它们的完美匹配和我们的猜测,可能也很有价值。
我们仅用几行代码就成功实现了一个可用的问答系统。如果你对所达到的结果感到满意,那么你可以立即开始使用它。不过,如果你觉得需要稍作改进,那么微调模型是一个不错的选择。如果你想查看完整的源代码,可以在 Google Colab 上找到。

