什么是三重态损失?
三重态损失最初在2015年的FaceNet:用于人脸识别和聚类的统一嵌入中提出,此后它一直是监督相似性或度量学习中最流行的损失函数之一。最简单的解释是,三重态损失鼓励不相似的对与任何相似的对之间至少存在一定的裕度值。数学上,损失值可以计算为 $L=max(d(a,p) - d(a,n) + m, 0)$,其中
- $p$,即正样本,是与 $a$(即锚点)具有相同标签的样本,
- $n$,即负样本,是另一个与 $a$ 具有不同标签的样本,
- $d$ 是衡量这三个样本之间距离的函数,
- 而 $m$ 是一个裕度值,用于使负样本保持足够远的距离。
该论文使用欧几里得距离,但使用任何其他距离度量(例如余弦距离)也同样有效。
该函数具有一个学习目标,可以如下图所示
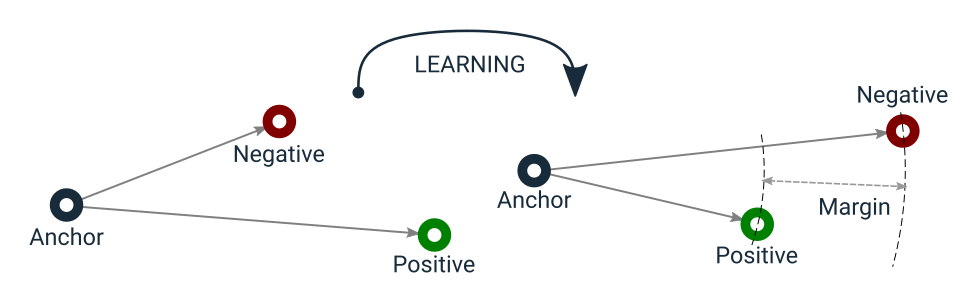
三重态损失学习目标
请注意,三重态损失不像对比损失那样具有将锚点和正样本编码到向量空间中同一点的副作用。这使得三重态损失能够容忍一些类内方差,不像对比损失那样,因为后者本质上强制锚点和任何正样本之间的距离为0。换句话说,三重态损失允许以一种方式拉伸聚类,以包括异常值,同时仍然确保来自不同聚类(例如,负对)的样本之间存在裕度。
此外,三重态损失不那么贪婪。与对比损失不同,当不同的样本容易与相似的样本区分开时,它就已经满足了。如果没有负样本的干扰,它不会改变正聚类中的距离。这是因为三重态损失试图确保负对距离与正对距离之间存在裕度。然而,对比损失仅在比较不相似的对时才考虑裕度值,并且根本不关心相似的对此刻在哪里。这意味着对比损失可能会更早达到局部最小值,而三重态损失可能会继续将向量空间组织到更好的状态。
让我们通过动画演示两种损失函数如何组织向量空间。为了简化可视化,向量由二维空间中的点表示,并且它们是从正态分布中随机选择的。
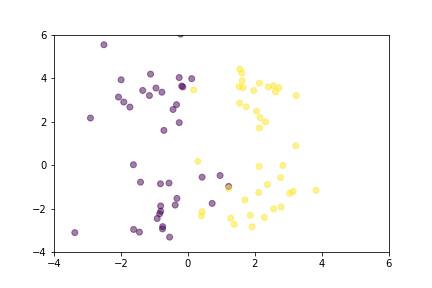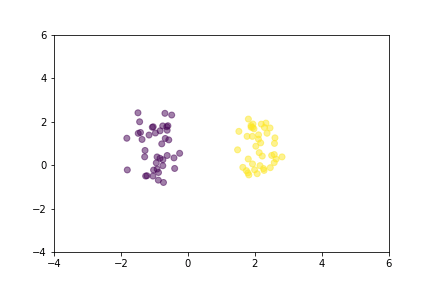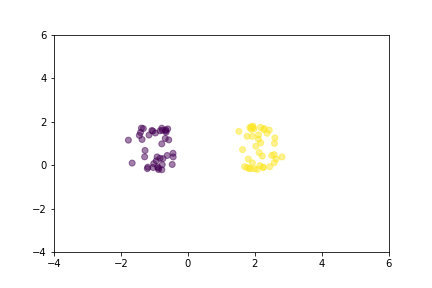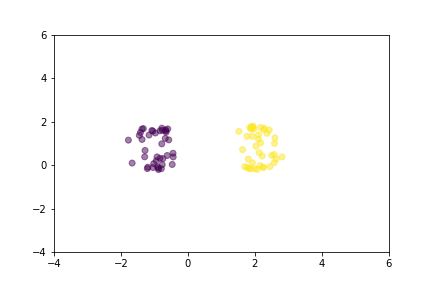
显示对比损失在训练过程中如何移动点的动画。

显示三重态损失在训练过程中如何移动点的动画。
从两种损失函数的数学解释来看,很明显三重态损失在理论上更强,但三重态损失还有额外的技巧可以帮助它更好地工作。最重要的是,三重态损失引入了在线三元组挖掘策略,例如自动形成最有用的三元组。
为什么三元组挖掘很重要?
三重态损失的公式表明它一次处理三个对象
锚点,正样本- 与锚点具有相同标签的样本,- 和
负样本- 与锚点和正样本具有不同标签的样本。
在朴素实现中,我们可以在每个 epoch 的开始形成这样的样本三元组,然后将批次的三元组馈送给模型。这称为“离线策略”。然而,由于以下几个原因,这效率不高
- 它需要传递 $3n$ 个样本才能得到 $n$ 个三元组的损失值。
- 并非所有这些三元组都对模型学习任何东西有用,例如,产生正损失值。
- 即使我们使用我将在本系列中实现的方法之一在每个 epoch 的开始形成“有用”的三元组,由于模型权重会不断更新,它们在 epoch 的某个点可能会变得“无用”。
相反,我们可以获取一批 $n$ 个样本及其关联的标签,并实时形成三元组。这称为“在线策略”。通常,这会产生 $n^3$ 个可能的三元组,但只有这些可能三元组的子集实际上是有效的。即使在这种情况下,我们将从比离线策略多得多的三元组中计算损失值。
给定一个三元组 (a, p, n),它仅在以下情况下有效
a和p具有相同的标签,a和p是不同的样本,- 并且
n与a和p具有不同的标签。
这些约束似乎需要使用嵌套循环进行昂贵的计算,但可以通过距离矩阵、掩码和广播等技巧高效实现。本系列的其余部分将重点介绍这些技巧的实现。
距离矩阵
距离矩阵是一个形状为 $(n, n)$ 的矩阵,用于存储两个 $n$ 大小集合中所有可能对之间的距离值。该矩阵可用于向量化否则需要低效循环的计算。其计算也可以优化,我们将实现由 Samuel Albanie 解释的欧几里得距离矩阵技巧 (PDF)。您可能希望阅读这份三页文档以全面了解该技巧的直觉,但简要解释如下
- 计算两组向量的点积,例如,在我们的例子中是嵌入。
- 从该矩阵中提取对角线,该对角线保存每个嵌入的欧几里得范数的平方。
- 根据以下方程计算平方欧几里得距离矩阵:$||a - b||^2 = ||a||^2 - 2 ⟨a, b⟩ + ||b||^2$
- 获取该矩阵的平方根以获得非平方距离。
我们将在 PyTorch 中实现它,所以让我们从导入开始。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
eps = 1e-8 # an arbitrary small value to be used for numerical stability tricks
def euclidean_distance_matrix(x):
"""Efficient computation of Euclidean distance matrix
Args:
x: Input tensor of shape (batch_size, embedding_dim)
Returns:
Distance matrix of shape (batch_size, batch_size)
"""
# step 1 - compute the dot product
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size)
dot_product = torch.mm(x, x.t())
# step 2 - extract the squared Euclidean norm from the diagonal
# shape: (batch_size,)
squared_norm = torch.diag(dot_product)
# step 3 - compute squared Euclidean distances
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size)
distance_matrix = squared_norm.unsqueeze(0) - 2 * dot_product + squared_norm.unsqueeze(1)
# get rid of negative distances due to numerical instabilities
distance_matrix = F.relu(distance_matrix)
# step 4 - compute the non-squared distances
# handle numerical stability
# derivative of the square root operation applied to 0 is infinite
# we need to handle by setting any 0 to eps
mask = (distance_matrix == 0.0).float()
# use this mask to set indices with a value of 0 to eps
distance_matrix += mask * eps
# now it is safe to get the square root
distance_matrix = torch.sqrt(distance_matrix)
# undo the trick for numerical stability
distance_matrix *= (1.0 - mask)
return distance_matrix
无效三元组掩码
现在我们可以计算批处理中所有可能的嵌入对的距离矩阵,我们可以应用广播来枚举所有可能三元组的距离差异,并将它们表示为形状为 (batch_size, batch_size, batch_size) 的张量。然而,如前所述,只有这些 $n^3$ 个三元组中的子集实际上是有效的,我们需要一个相应的掩码来正确计算损失值。我们将分三步实现这样一个辅助函数
- 计算不同索引的掩码,例如
(i != j 和 j != k)。 - 计算有效锚点-正样本-负样本三元组的掩码,例如
labels[i] == labels[j] 和 labels[j] != labels[k]。 - 组合两个掩码。
def get_triplet_mask(labels):
"""compute a mask for valid triplets
Args:
labels: Batch of integer labels. shape: (batch_size,)
Returns:
Mask tensor to indicate which triplets are actually valid. Shape: (batch_size, batch_size, batch_size)
A triplet is valid if:
`labels[i] == labels[j] and labels[i] != labels[k]`
and `i`, `j`, `k` are different.
"""
# step 1 - get a mask for distinct indices
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size)
indices_equal = torch.eye(labels.size()[0], dtype=torch.bool, device=labels.device)
indices_not_equal = torch.logical_not(indices_equal)
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size, 1)
i_not_equal_j = indices_not_equal.unsqueeze(2)
# shape: (batch_size, 1, batch_size)
i_not_equal_k = indices_not_equal.unsqueeze(1)
# shape: (1, batch_size, batch_size)
j_not_equal_k = indices_not_equal.unsqueeze(0)
# Shape: (batch_size, batch_size, batch_size)
distinct_indices = torch.logical_and(torch.logical_and(i_not_equal_j, i_not_equal_k), j_not_equal_k)
# step 2 - get a mask for valid anchor-positive-negative triplets
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size)
labels_equal = labels.unsqueeze(0) == labels.unsqueeze(1)
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size, 1)
i_equal_j = labels_equal.unsqueeze(2)
# shape: (batch_size, 1, batch_size)
i_equal_k = labels_equal.unsqueeze(1)
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size, batch_size)
valid_indices = torch.logical_and(i_equal_j, torch.logical_not(i_equal_k))
# step 3 - combine two masks
mask = torch.logical_and(distinct_indices, valid_indices)
return mask
在线三元组挖掘的批处理全策略
现在我们准备好实际实现三重态损失本身了。三重态损失涉及几种形成或选择三元组的策略,最简单的一种是使用批处理中样本可以形成的所有有效三元组。由于我们已经实现的实用函数,这可以通过四个简单的步骤实现
- 获取批处理中嵌入可以形成的所有可能对的距离矩阵。
- 对该矩阵应用广播以计算所有可能三元组的损失值。
- 将无效或简单三元组的损失值设置为 $0$。
- 平均剩余的正值以返回标量损失。
我将从实现此策略开始,更复杂的策略将在单独的帖子中介绍。
class BatchAllTtripletLoss(nn.Module):
"""Uses all valid triplets to compute Triplet loss
Args:
margin: Margin value in the Triplet Loss equation
"""
def __init__(self, margin=1.):
super().__init__()
self.margin = margin
def forward(self, embeddings, labels):
"""computes loss value.
Args:
embeddings: Batch of embeddings, e.g., output of the encoder. shape: (batch_size, embedding_dim)
labels: Batch of integer labels associated with embeddings. shape: (batch_size,)
Returns:
Scalar loss value.
"""
# step 1 - get distance matrix
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size)
distance_matrix = euclidean_distance_matrix(embeddings)
# step 2 - compute loss values for all triplets by applying broadcasting to distance matrix
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size, 1)
anchor_positive_dists = distance_matrix.unsqueeze(2)
# shape: (batch_size, 1, batch_size)
anchor_negative_dists = distance_matrix.unsqueeze(1)
# get loss values for all possible n^3 triplets
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size, batch_size)
triplet_loss = anchor_positive_dists - anchor_negative_dists + self.margin
# step 3 - filter out invalid or easy triplets by setting their loss values to 0
# shape: (batch_size, batch_size, batch_size)
mask = get_triplet_mask(labels)
triplet_loss *= mask
# easy triplets have negative loss values
triplet_loss = F.relu(triplet_loss)
# step 4 - compute scalar loss value by averaging positive losses
num_positive_losses = (triplet_loss > eps).float().sum()
triplet_loss = triplet_loss.sum() / (num_positive_losses + eps)
return triplet_loss
结论
我提到三重态损失不仅在数学上而且在样本选择策略上都与对比损失不同,并且我在这篇文章中通过使用几个技巧高效地实现了在线三元组挖掘的批处理全策略。
还有其他更复杂的策略,例如批处理硬挖掘和批处理半硬挖掘,但它们的实现以及对我在本文中为提高效率而使用的技巧的讨论值得单独的帖子。
未来的帖子将涵盖此类主题以及关于避免向量崩溃和控制类内和类间方差的一些技巧的额外讨论。

