探索数据
掌握了搜索中的概念后,您可以开始以其他方式探索数据。Qdrant 提供了一系列 API,允许您以不同方式查找相似向量,以及查找最不相似的向量。这些是推荐系统、数据探索和数据清理的有用工具。
推荐 API
除了常规搜索,Qdrant 还允许您基于多个正例和反例进行搜索。该 API 称为 recommend,示例可以是点 ID,这样您就可以利用已经编码的对象;而且,自 v1.6 起,您还可以使用原始向量作为输入,这样您就可以即时创建向量而无需将其作为点上传。
REST API - API 模式定义可在此处获取 here
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"recommend": {
"positive": [100, 231],
"negative": [718, [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
"strategy": "average_vector"
}
},
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"value": "London"
}
}
]
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.RecommendQuery(
recommend=models.RecommendInput(
positive=[100, 231],
negative=[718, [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
strategy=models.RecommendStrategy.AVERAGE_VECTOR,
)
),
query_filter=models.Filter(
must=[
models.FieldCondition(
key="city",
match=models.MatchValue(
value="London",
),
)
]
),
limit=3,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
recommend: {
positive: [100, 231],
negative: [718, [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
strategy: "average_vector"
}
},
filter: {
must: [
{
key: "city",
match: {
value: "London",
},
},
],
},
limit: 3
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
Condition, Filter, QueryPointsBuilder, RecommendInputBuilder, RecommendStrategy,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(
RecommendInputBuilder::default()
.add_positive(100)
.add_positive(231)
.add_positive(vec![0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5])
.add_negative(718)
.strategy(RecommendStrategy::AverageVector)
.build(),
)
.limit(3)
.filter(Filter::must([Condition::matches(
"city",
"London".to_string(),
)])),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.RecommendInput;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.RecommendStrategy;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Common.Filter;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeyword;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorInputFactory.vectorInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.recommend;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(recommend(RecommendInput.newBuilder()
.addAllPositive(List.of(vectorInput(100), vectorInput(200), vectorInput(100.0f, 231.0f)))
.addAllNegative(List.of(vectorInput(718), vectorInput(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f)))
.setStrategy(RecommendStrategy.AverageVector)
.build()))
.setFilter(Filter.newBuilder().addMust(matchKeyword("city", "London")))
.setLimit(3)
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new RecommendInput {
Positive = { 100, 231 },
Negative = { 718 }
},
filter: MatchKeyword("city", "London"),
limit: 3
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryRecommend(&qdrant.RecommendInput{
Positive: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(100)),
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(231)),
},
Negative: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(718)),
},
}),
Filter: &qdrant.Filter{
Must: []*qdrant.Condition{
qdrant.NewMatch("city", "London"),
},
},
})
此 API 的示例结果将是
{
"result": [
{ "id": 10, "score": 0.81 },
{ "id": 14, "score": 0.75 },
{ "id": 11, "score": 0.73 }
],
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}
用于获取推荐的算法从可用的 strategy 选项中选择。每个选项都有其自身的优缺点,因此请进行实验并选择最适合您案例的选项。
平均向量策略
Qdrant 中默认且首先添加的策略称为 average_vector。它预处理输入示例以创建一个用于搜索的单个向量。由于预处理步骤发生得非常快,因此该策略的性能与常规搜索相当。这种推荐背后的直觉是每个向量分量代表数据的一个独立特征,因此,通过平均示例,我们应该得到一个好的推荐。
生成搜索向量的方法是首先分别平均所有正例和反例,然后使用以下公式将它们组合成一个单个向量
avg_positive + avg_positive - avg_negative
如果没有反例,则搜索向量将简单地等于 avg_positive。
这是将隐式设置的默认策略,但您可以在推荐请求中设置 "strategy": "average_vector" 来明确定义它。
最佳分数策略
自 v1.6.0 起可用
v1.6 中引入的一种新策略称为 best_score。它基于以下思想:查找相似向量的最佳方法是查找更接近正例的向量,同时避免更接近反例的向量。它的工作原理是,每个候选向量都与每个示例进行度量,然后我们选择最佳正分数和最佳负分数。最终分数通过以下步骤公式选择
// Sigmoid function to normalize the score between 0 and 1
let sigmoid = |x| 0.5 * (1.0 + (x / (1.0 + x.abs())));
let score = if best_positive_score > best_negative_score {
sigmoid(best_positive_score)
} else {
-sigmoid(best_negative_score)
};
由于我们在搜索的每个步骤中计算与每个示例的相似性,因此此策略的性能将受到示例数量的线性影响。这意味着您提供的示例越多,搜索速度就越慢。然而,此策略可能非常强大,并且应该更与嵌入无关。
要使用此算法,您需要在推荐请求中设置 "strategy": "best_score"。
仅使用反例
best_score 策略的一个有益的副作用是您可以仅将其与反例一起使用。这将允许您找到与您提供的向量最不相似的向量。这对于在数据中查找异常值,或者查找与给定向量最不相似的向量可能很有用。
将仅反例与过滤相结合是数据探索和清理的强大工具。
分数求和策略
同时使用多个查询向量的另一种策略是简单地将它们与候选向量的分数相加。在 qdrant 中,这称为 sum_scores 策略。
UKP Lab、hessian.ai 和 cohere.ai 在这篇论文中使用了该策略,将相关性反馈整合到后续搜索中。在论文中,当使用 2-8 个正反馈文档时,这使得 nDCG@20 性能提高了 5.6% 个百分点。
此策略实现的公式是
$$ s_i = \sum_{v_q\in Q^+}s(v_q, v_i) - \sum_{v_q\in Q^-}s(v_q, v_i) $$
其中 $Q^+$ 是正例集合,$Q^-$ 是反例集合,$s(v_q, v_i)$ 是向量 $v_q$ 与向量 $v_i$ 的得分
与 best_score 一样,此策略也允许仅使用反例。
多个向量
自 v0.10.0 起可用
如果集合是使用多个向量创建的,则应在推荐请求中指定向量的名称
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"recommend": {
"positive": [100, 231],
"negative": [718]
}
},
"using": "image",
"limit": 10
}
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.RecommendQuery(
recommend=models.RecommendInput(
positive=[100, 231],
negative=[718],
)
),
using="image",
limit=10,
)
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
recommend: {
positive: [100, 231],
negative: [718],
}
},
using: "image",
limit: 10
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{QueryPointsBuilder, RecommendInputBuilder};
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(
RecommendInputBuilder::default()
.add_positive(100)
.add_positive(231)
.add_negative(718)
.build(),
)
.limit(10)
.using("image"),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.RecommendInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorInputFactory.vectorInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.recommend;
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(recommend(RecommendInput.newBuilder()
.addAllPositive(List.of(vectorInput(100), vectorInput(231)))
.addAllNegative(List.of(vectorInput(718)))
.build()))
.setUsing("image")
.setLimit(10)
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new RecommendInput {
Positive = { 100, 231 },
Negative = { 718 }
},
usingVector: "image",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryRecommend(&qdrant.RecommendInput{
Positive: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(100)),
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(231)),
},
Negative: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(718)),
},
}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("image"),
})
参数 using 指定要用于推荐的存储向量。
从另一个集合查找向量
自 v0.11.6 起可用
如果您的集合具有相同维度的向量,并且您想根据另一个集合的向量在一个集合中查找推荐,您可以使用 lookup_from 参数。
这可能很有用,例如在项目到用户的推荐场景中。在这种场景中,用户和项目嵌入,尽管具有相同的向量参数(距离类型和维度),但通常存储在不同的集合中。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"recommend": {
"positive": [100, 231],
"negative": [718]
}
},
"limit": 10,
"lookup_from": {
"collection": "{external_collection_name}",
"vector": "{external_vector_name}"
}
}
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.RecommendQuery(
recommend=models.RecommendInput(
positive=[100, 231],
negative=[718],
)
),
using="image",
limit=10,
lookup_from=models.LookupLocation(
collection="{external_collection_name}", vector="{external_vector_name}"
),
)
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
recommend: {
positive: [100, 231],
negative: [718],
}
},
using: "image",
limit: 10,
lookup_from: {
collection: "{external_collection_name}",
vector: "{external_vector_name}"
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{LookupLocationBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder, RecommendInputBuilder};
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(
RecommendInputBuilder::default()
.add_positive(100)
.add_positive(231)
.add_negative(718)
.build(),
)
.limit(10)
.using("image")
.lookup_from(
LookupLocationBuilder::new("{external_collection_name}")
.vector_name("{external_vector_name}"),
),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.LookupLocation;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.RecommendInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorInputFactory.vectorInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.recommend;
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(recommend(RecommendInput.newBuilder()
.addAllPositive(List.of(vectorInput(100), vectorInput(231)))
.addAllNegative(List.of(vectorInput(718)))
.build()))
.setUsing("image")
.setLimit(10)
.setLookupFrom(
LookupLocation.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{external_collection_name}")
.setVectorName("{external_vector_name}")
.build())
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new RecommendInput {
Positive = { 100, 231 },
Negative = { 718 }
},
usingVector: "image",
limit: 10,
lookupFrom: new LookupLocation
{
CollectionName = "{external_collection_name}",
VectorName = "{external_vector_name}",
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryRecommend(&qdrant.RecommendInput{
Positive: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(100)),
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(231)),
},
Negative: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(718)),
},
}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("image"),
LookupFrom: &qdrant.LookupLocation{
CollectionName: "{external_collection_name}",
VectorName: qdrant.PtrOf("{external_vector_name}"),
},
})
向量通过 positive 和 negative 列表中提供的 ID 从外部集合中检索。然后,这些向量用于在当前集合中执行推荐,并与“using”向量或默认向量进行比较。
批量推荐 API
自 v0.10.0 起可用
与批量搜索 API 在用法和优点上相似,它支持批量推荐请求。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/query/batch
{
"searches": [
{
"query": {
"recommend": {
"positive": [100, 231],
"negative": [718]
}
},
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"value": "London"
}
}
]
},
"limit": 10
},
{
"query": {
"recommend": {
"positive": [200, 67],
"negative": [300]
}
},
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"value": "London"
}
}
]
},
"limit": 10
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
filter_ = models.Filter(
must=[
models.FieldCondition(
key="city",
match=models.MatchValue(
value="London",
),
)
]
)
recommend_queries = [
models.QueryRequest(
query=models.RecommendQuery(
recommend=models.RecommendInput(positive=[100, 231], negative=[718])
),
filter=filter_,
limit=3,
),
models.QueryRequest(
query=models.RecommendQuery(
recommend=models.RecommendInput(positive=[200, 67], negative=[300])
),
filter=filter_,
limit=3,
),
]
client.query_batch_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}", requests=recommend_queries
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const filter = {
must: [
{
key: "city",
match: {
value: "London",
},
},
],
};
const searches = [
{
query: {
recommend: {
positive: [100, 231],
negative: [718]
}
},
filter,
limit: 3,
},
{
query: {
recommend: {
positive: [200, 67],
negative: [300]
}
},
filter,
limit: 3,
},
];
client.queryBatch("{collection_name}", {
searches,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
Condition, Filter, QueryBatchPointsBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder,
RecommendInputBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
let filter = Filter::must([Condition::matches("city", "London".to_string())]);
let recommend_queries = vec![
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(
RecommendInputBuilder::default()
.add_positive(100)
.add_positive(231)
.add_negative(718)
.build(),
)
.filter(filter.clone())
.build(),
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(
RecommendInputBuilder::default()
.add_positive(200)
.add_positive(67)
.add_negative(300)
.build(),
)
.filter(filter)
.build(),
];
client
.query_batch(QueryBatchPointsBuilder::new(
"{collection_name}",
recommend_queries,
))
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Common.Filter;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.RecommendInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeyword;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorInputFactory.vectorInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.recommend;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
Filter filter = Filter.newBuilder().addMust(matchKeyword("city", "London")).build();
List<QueryPoints> recommendQueries = List.of(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(recommend(
RecommendInput.newBuilder()
.addAllPositive(List.of(vectorInput(100), vectorInput(231)))
.addAllNegative(List.of(vectorInput(731)))
.build()))
.setFilter(filter)
.setLimit(3)
.build(),
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(recommend(
RecommendInput.newBuilder()
.addAllPositive(List.of(vectorInput(200), vectorInput(67)))
.addAllNegative(List.of(vectorInput(300)))
.build()))
.setFilter(filter)
.setLimit(3)
.build());
client.queryBatchAsync("{collection_name}", recommendQueries).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
var filter = MatchKeyword("city", "london");
await client.QueryBatchAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
queries:
[
new QueryPoints()
{
CollectionName = "{collection_name}",
Query = new RecommendInput {
Positive = { 100, 231 },
Negative = { 718 },
},
Limit = 3,
Filter = filter,
},
new QueryPoints()
{
CollectionName = "{collection_name}",
Query = new RecommendInput {
Positive = { 200, 67 },
Negative = { 300 },
},
Limit = 3,
Filter = filter,
}
]
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
filter := qdrant.Filter{
Must: []*qdrant.Condition{
qdrant.NewMatch("city", "London"),
},
}
client.QueryBatch(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryBatchPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
QueryPoints: []*qdrant.QueryPoints{
{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryRecommend(&qdrant.RecommendInput{
Positive: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(100)),
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(231)),
},
Negative: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(718)),
},
},
),
Filter: &filter,
},
{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryRecommend(&qdrant.RecommendInput{
Positive: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(200)),
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(67)),
},
Negative: []*qdrant.VectorInput{
qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(300)),
},
},
),
Filter: &filter,
},
},
},
)
此 API 的结果为每个推荐请求包含一个数组。
{
"result": [
[
{ "id": 10, "score": 0.81 },
{ "id": 14, "score": 0.75 },
{ "id": 11, "score": 0.73 }
],
[
{ "id": 1, "score": 0.92 },
{ "id": 3, "score": 0.89 },
{ "id": 9, "score": 0.75 }
]
],
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}
发现 API
自 v1.7 起可用
REST API 模式定义可在此处获取 here
在此 API 中,Qdrant 引入了 context 的概念,它用于划分空间。上下文是一组正负对,每对将空间划分为正负区域。在这种模式下,搜索操作根据点所属的正区域数量(或它们避免负区域的程度)来优先选择点。
提供上下文的接口类似于推荐 API(ID 或原始向量)。但是,在这种情况下,它们需要以正负对的形式提供。
发现 API 允许您执行两种新的搜索类型
- 发现搜索:使用上下文(正负向量对)和目标返回与目标更相似但受上下文约束的点。
- 上下文搜索:仅使用上下文对,获取位于最佳区域(损失最小化)的点
正负示例在上下文对中的排列方式完全取决于您。因此,您可以根据您的模型和数据灵活地尝试不同的排列技术。
发现搜索
这种类型的搜索在结合多模态、向量约束搜索方面效果特别好。Qdrant 已经对过滤器提供了广泛的支持,这些过滤器根据其负载约束搜索,但使用发现搜索,您还可以约束执行搜索的向量空间。
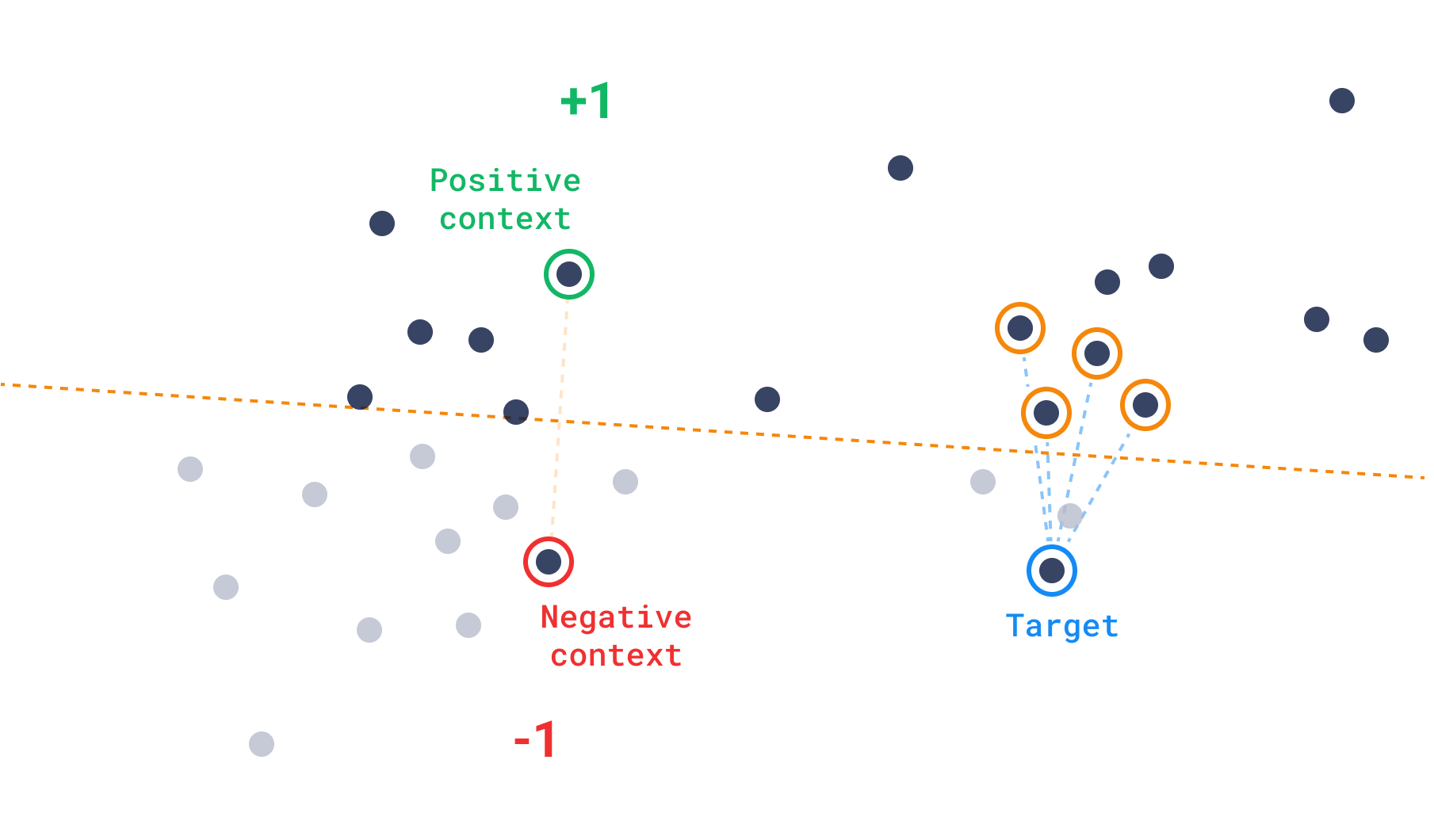
发现分数的公式可以表示为
$$ \text{rank}(v^+, v^-) = \begin{cases} 1, &\quad s(v^+) \geq s(v^-) \\ -1, &\quad s(v^+) < s(v^-) \end{cases} $$ 其中 $v^+$ 表示一个正例,$v^-$ 表示一个负例,$s(v)$ 是向量 $v$ 与目标向量的相似度得分。然后计算发现得分: $$ \text{discovery score} = \text{sigmoid}(s(v_t))+ \sum \text{rank}(v_i^+, v_i^-), $$ 其中 $s(v)$ 是相似度函数,$v_t$ 是目标向量,并且 $v_i^+$ 和 $v_i^-$ 分别是正例和负例。sigmoid 函数用于将得分归一化到 0 到 1 之间,等级之和用于惩罚那些比正例更接近负例的向量。换句话说,各个等级之和决定了一个点处于多少个正区域中,而接近度层次则排在第二位。
示例
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"discover": {
"target": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"context": [
{
"positive": 100,
"negative": 718
},
{
"positive": 200,
"negative": 300
}
]
}
},
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
discover_queries = [
models.QueryRequest(
query=models.DiscoverQuery(
discover=models.DiscoverInput(
target=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
context=[
models.ContextPair(
positive=100,
negative=718,
),
models.ContextPair(
positive=200,
negative=300,
),
],
)
),
limit=10,
),
]
client.query_batch_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}", requests=discover_queries
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
discover: {
target: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
context: [
{
positive: 100,
negative: 718,
},
{
positive: 200,
negative: 300,
},
],
}
},
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{ContextInputBuilder, DiscoverInputBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}").query(
DiscoverInputBuilder::new(
vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
ContextInputBuilder::default()
.add_pair(100, 718)
.add_pair(200, 300),
)
.build(),
),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.ContextInput;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.ContextInputPair;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.DiscoverInput;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorInputFactory.vectorInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.discover;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(discover(DiscoverInput.newBuilder()
.setTarget(vectorInput(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setContext(ContextInput.newBuilder()
.addAllPairs(List.of(
ContextInputPair.newBuilder()
.setPositive(vectorInput(100))
.setNegative(vectorInput(718))
.build(),
ContextInputPair.newBuilder()
.setPositive(vectorInput(200))
.setNegative(vectorInput(300))
.build()))
.build())
.build()))
.setLimit(10)
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new DiscoverInput {
Target = new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
Context = new ContextInput {
Pairs = {
new ContextInputPair {
Positive = 100,
Negative = 718
},
new ContextInputPair {
Positive = 200,
Negative = 300
},
}
},
},
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDiscover(&qdrant.DiscoverInput{
Target: qdrant.NewVectorInput(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
Context: &qdrant.ContextInput{
Pairs: []*qdrant.ContextInputPair{
{
Positive: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(100)),
Negative: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(718)),
},
{
Positive: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(200)),
Negative: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(300)),
},
},
},
}),
})
上下文搜索
相反,在没有目标的情况下,在使用 HNSW 等邻近图时,刚性逐整数函数并不能为搜索提供太多指导。相反,上下文搜索采用了一个源自三重损失概念的函数,该函数通常在模型训练期间应用。对于上下文搜索,此函数经过调整以引导搜索到负例较少的区域。
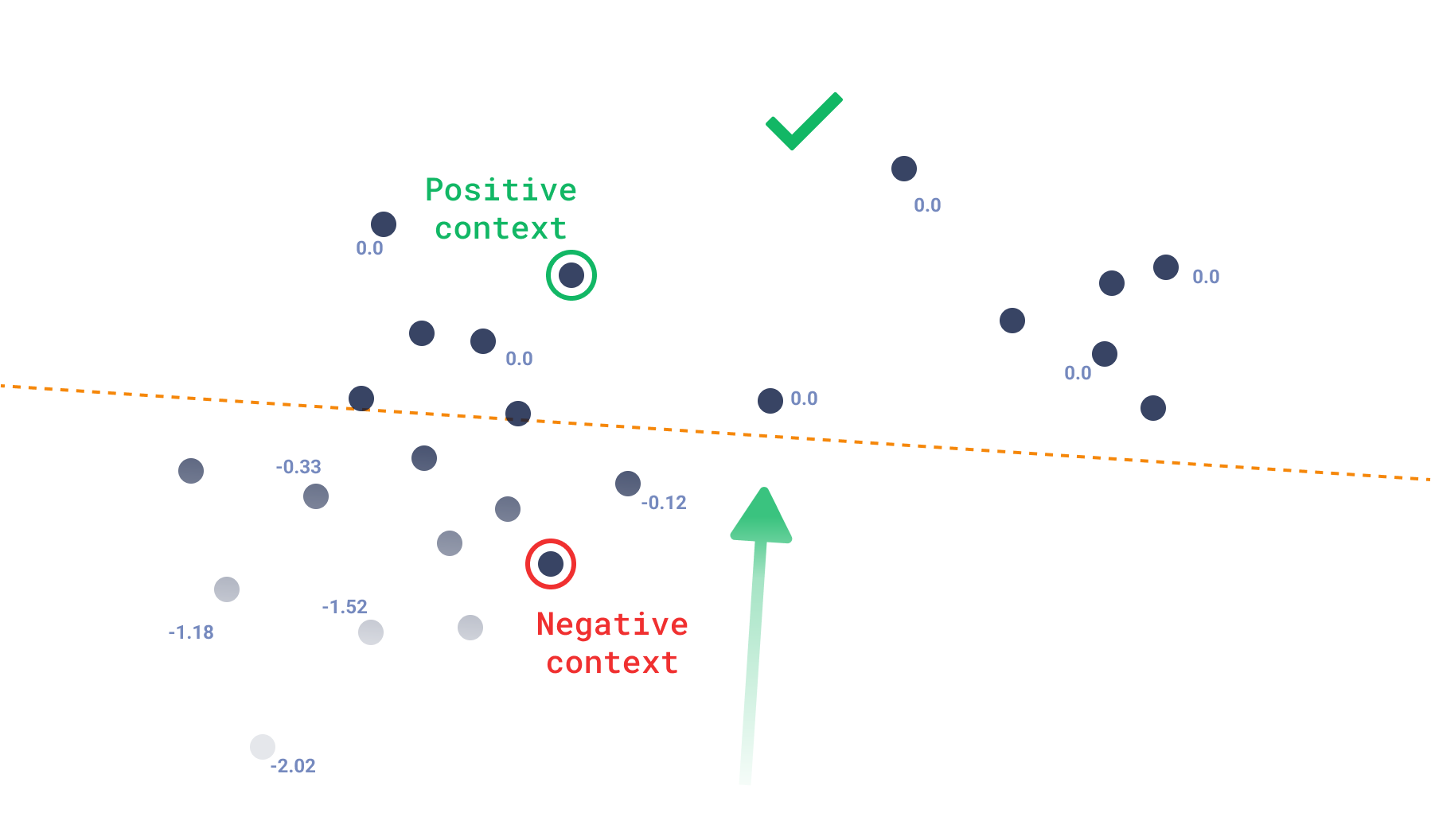
我们可以将得分函数直接与损失函数关联起来,其中 0.0 是点可以拥有的最大得分,这意味着它仅存在于正区域。一旦点存在更接近负例,其损失将简单地是正相似度和负相似度之差。
$$ \text{context score} = \sum \min(s(v^+_i) - s(v^-_i), 0.0) $$
其中 $v^+_i$ 和 $v^-_i$ 是每对的正例和反例,$s(v)$ 是相似度函数。
使用这种搜索,您可以预期输出不一定围绕单个点,而是任何不更接近反例的点,这会创建受约束的多样化结果。因此,即使 API 不被称为recommend,推荐系统也可以使用这种方法并根据其特定用例进行调整。
示例
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"context": [
{
"positive": 100,
"negative": 718
},
{
"positive": 200,
"negative": 300
}
]
},
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
discover_queries = [
models.QueryRequest(
query=models.ContextQuery(
context=[
models.ContextPair(
positive=100,
negative=718,
),
models.ContextPair(
positive=200,
negative=300,
),
],
),
limit=10,
),
]
client.query_batch_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}", requests=discover_queries
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
context: [
{
positive: 100,
negative: 718,
},
{
positive: 200,
negative: 300,
},
]
},
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{ContextInputBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}").query(
ContextInputBuilder::default()
.add_pair(100, 718)
.add_pair(200, 300)
.build(),
),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.ContextInput;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.ContextInputPair;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorInputFactory.vectorInput;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.context;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(context(ContextInput.newBuilder()
.addAllPairs(List.of(
ContextInputPair.newBuilder()
.setPositive(vectorInput(100))
.setNegative(vectorInput(718))
.build(),
ContextInputPair.newBuilder()
.setPositive(vectorInput(200))
.setNegative(vectorInput(300))
.build()))
.build()))
.setLimit(10)
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new ContextInput {
Pairs = {
new ContextInputPair {
Positive = 100,
Negative = 718
},
new ContextInputPair {
Positive = 200,
Negative = 300
},
}
},
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryContext(&qdrant.ContextInput{
Pairs: []*qdrant.ContextInputPair{
{
Positive: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(100)),
Negative: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(718)),
},
{
Positive: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(200)),
Negative: qdrant.NewVectorInputID(qdrant.NewIDNum(300)),
},
},
}),
})
距离矩阵
自 v1.12.0 起可用
距离矩阵 API 允许计算采样向量对之间的距离,并将结果以稀疏矩阵的形式返回。
此类 API 支持新的数据探索用例,例如相似向量的聚类、连接的可视化或降维。
API 输入请求包含以下参数
sample:要采样的向量数量limit:每个样本要返回的分数数量filter:应用于约束样本的过滤器
让我们看一个使用 sample=100,limit=10 的基本示例
引擎首先从集合中选择 100 个随机点,然后对于每个选定的点,它将计算样本中前 10 个最近的点。
这将导致总共 1000 个分数,表示为稀疏矩阵以进行高效处理。
距离矩阵 API 提供两种输出格式,以方便与不同工具集成。
成对格式
将距离矩阵作为点 ids 对的列表及其各自的分数返回。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/search/matrix/pairs
{
"sample": 10,
"limit": 2,
"filter": {
"must": {
"key": "color",
"match": { "value": "red" }
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.search_matrix_pairs(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
sample=10,
limit=2,
query_filter=models.Filter(
must=[
models.FieldCondition(
key="color", match=models.MatchValue(value="red")
),
]
),
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.searchMatrixPairs("{collection_name}", {
filter: {
must: [
{
key: "color",
match: {
value: "red",
},
},
],
},
sample: 10,
limit: 2,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Condition, Filter, SearchMatrixPointsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
client
.search_matrix_pairs(
SearchMatrixPointsBuilder::new("collection_name")
.filter(Filter::must(vec![Condition::matches(
"color",
"red".to_string(),
)]))
.sample(10)
.limit(2),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeyword;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Common.Filter;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SearchMatrixPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.searchMatrixPairsAsync(
Points.SearchMatrixPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setFilter(Filter.newBuilder().addMust(matchKeyword("color", "red")).build())
.setSample(10)
.setLimit(2)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.SearchMatrixPairsAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
filter: MatchKeyword("color", "red"),
sample: 10,
limit: 2
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
sample := uint64(10)
limit := uint64(2)
res, err := client.SearchMatrixPairs(ctx, &qdrant.SearchMatrixPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Sample: &sample,
Limit: &limit,
Filter: &qdrant.Filter{
Must: []*qdrant.Condition{
qdrant.NewMatch("color", "red"),
},
},
})
返回
{
"result": {
"pairs": [
{"a": 1, "b": 3, "score": 1.4063001},
{"a": 1, "b": 4, "score": 1.2531},
{"a": 2, "b": 1, "score": 1.1550001},
{"a": 2, "b": 8, "score": 1.1359},
{"a": 3, "b": 1, "score": 1.4063001},
{"a": 3, "b": 4, "score": 1.2218001},
{"a": 4, "b": 1, "score": 1.2531},
{"a": 4, "b": 3, "score": 1.2218001},
{"a": 5, "b": 3, "score": 0.70239997},
{"a": 5, "b": 1, "score": 0.6146},
{"a": 6, "b": 3, "score": 0.6353},
{"a": 6, "b": 4, "score": 0.5093},
{"a": 7, "b": 3, "score": 1.0990001},
{"a": 7, "b": 1, "score": 1.0349001},
{"a": 8, "b": 2, "score": 1.1359},
{"a": 8, "b": 3, "score": 1.0553}
]
}
}
偏移量格式
将距离矩阵作为四个数组返回
offsets_row和offsets_col表示矩阵中非零距离值的位置。scores包含距离值。ids包含与距离值对应的点 ID。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/search/matrix/offsets
{
"sample": 10,
"limit": 2,
"filter": {
"must": {
"key": "color",
"match": { "value": "red" }
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.search_matrix_offsets(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
sample=10,
limit=2,
query_filter=models.Filter(
must=[
models.FieldCondition(
key="color", match=models.MatchValue(value="red")
),
]
),
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.searchMatrixOffsets("{collection_name}", {
filter: {
must: [
{
key: "color",
match: {
value: "red",
},
},
],
},
sample: 10,
limit: 2,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Condition, Filter, SearchMatrixPointsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
client
.search_matrix_offsets(
SearchMatrixPointsBuilder::new("collection_name")
.filter(Filter::must(vec![Condition::matches(
"color",
"red".to_string(),
)]))
.sample(10)
.limit(2),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeyword;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Common.Filter;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SearchMatrixPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.searchMatrixOffsetsAsync(
SearchMatrixPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setFilter(Filter.newBuilder().addMust(matchKeyword("color", "red")).build())
.setSample(10)
.setLimit(2)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.SearchMatrixOffsetsAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
filter: MatchKeyword("color", "red"),
sample: 10,
limit: 2
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
sample := uint64(10)
limit := uint64(2)
res, err := client.SearchMatrixOffsets(ctx, &qdrant.SearchMatrixPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Sample: &sample,
Limit: &limit,
Filter: &qdrant.Filter{
Must: []*qdrant.Condition{
qdrant.NewMatch("color", "red"),
},
},
})
返回
{
"result": {
"offsets_row": [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7],
"offsets_col": [2, 3, 0, 7, 0, 3, 0, 2, 2, 0, 2, 3, 2, 0, 1, 2],
"scores": [
1.4063001, 1.2531, 1.1550001, 1.1359, 1.4063001,
1.2218001, 1.2531, 1.2218001, 0.70239997, 0.6146, 0.6353,
0.5093, 1.0990001, 1.0349001, 1.1359, 1.0553
],
"ids": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
}
}
