混合和多阶段查询
自 v1.10.0 起可用
随着每个点多个命名向量的引入,在某些用例中,通过组合多个查询或分多个阶段执行搜索可以获得最佳搜索结果。
Qdrant 拥有一个灵活通用的接口来实现这一点,称为 Query API(API 参考)。
实现查询组合的主要组件是 prefetch 参数,它支持进行子请求。
具体来说,只要查询至少包含一个预取(prefetch),Qdrant 就会:
- 执行预取查询(或多个查询),
- 在其预取结果上应用主查询。
此外,预取本身也可以包含预取,因此您可以拥有嵌套的预取。
混合搜索
当您有相同数据的不同表示时,最常见的问题之一是将每种表示的查询点合并为一个结果。
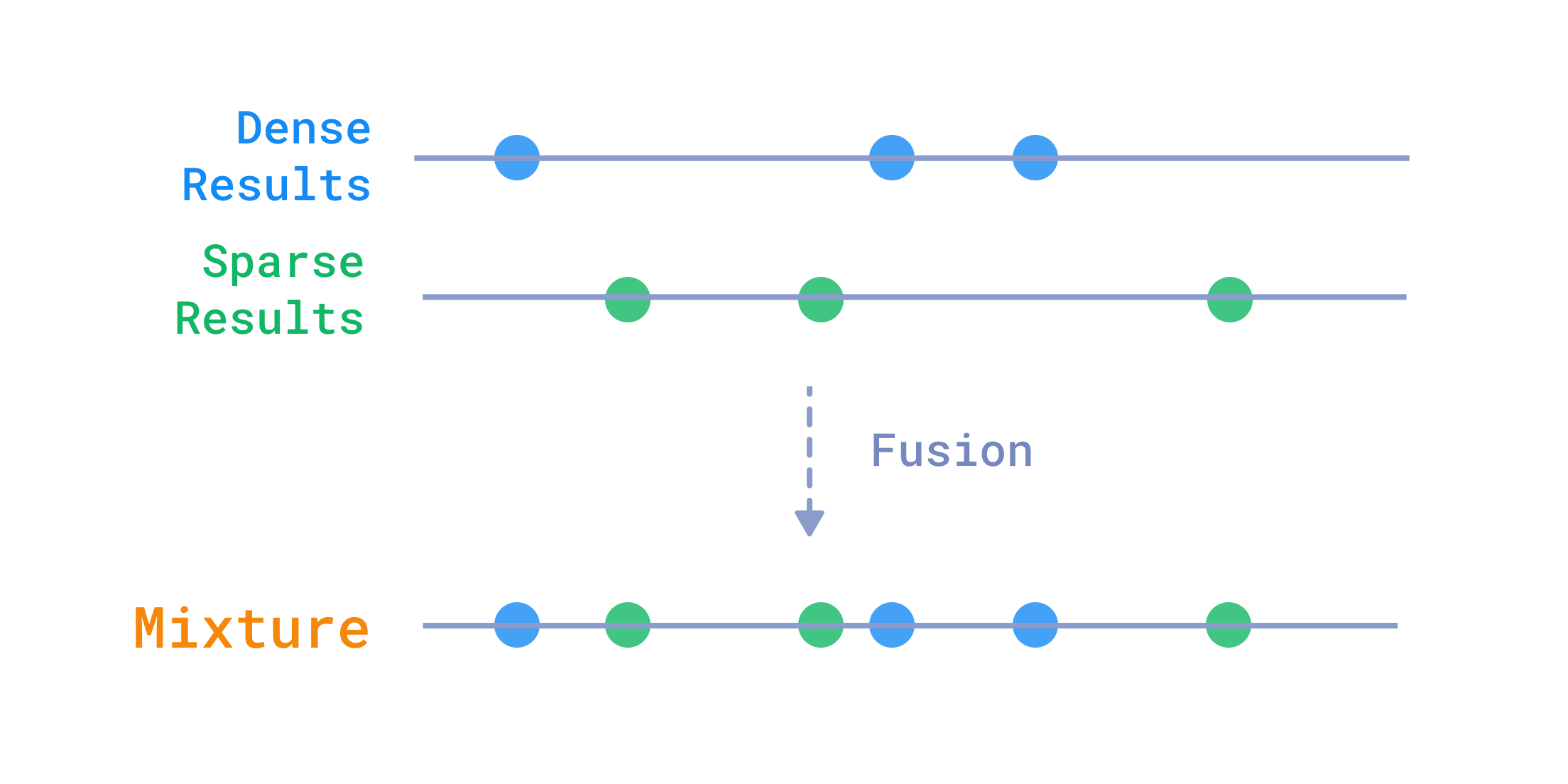
融合来自多个查询的结果
例如,在文本搜索中,结合密集向量和稀疏向量通常很有用,可以同时获得两者的优点:密集向量提供语义理解,稀疏向量提供精确的单词匹配。
Qdrant 有几种融合不同查询结果的方法:rrf 和 dbsf
倒数排名融合(RRF)
RRF 考虑结果在每个查询中的位置,并提升在多个结果集中都靠前的结果。公式很简单,但需要访问每个结果在每个查询中的排名。
$$ score(d\in D) = \sum_{r_d\in R(d)} \frac{1}{k + r_d} $$
其中 $D$ 是所有结果中的点集,$R(d)$ 是特定文档的排名集,$k$ 是一个常数(默认为 2)。
这是一个 RRF 示例,其中查询包含两个预取,分别针对配置为存储稀疏向量和密集向量的不同命名向量。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": [
{
"query": {
"indices": [1, 42], // <┐
"values": [0.22, 0.8] // <┴─sparse vector
},
"using": "sparse",
"limit": 20
},
{
"query": [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- dense vector
"using": "dense",
"limit": 20
}
],
"query": { "fusion": "rrf" }, // <--- reciprocal rank fusion
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=[
models.Prefetch(
query=models.SparseVector(indices=[1, 42], values=[0.22, 0.8]),
using="sparse",
limit=20,
),
models.Prefetch(
query=[0.01, 0.45, 0.67], # <-- dense vector
using="dense",
limit=20,
),
],
query=models.FusionQuery(fusion=models.Fusion.RRF),
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: [
{
query: {
values: [0.22, 0.8],
indices: [1, 42],
},
using: 'sparse',
limit: 20,
},
{
query: [0.01, 0.45, 0.67],
using: 'dense',
limit: 20,
},
],
query: {
fusion: 'rrf',
},
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Fusion, PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest([(1, 0.22), (42, 0.8)].as_slice()))
.using("sparse")
.limit(20u64)
)
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67]))
.using("dense")
.limit(20u64)
)
.query(Query::new_fusion(Fusion::Rrf))
).await?;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.fusion;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Fusion;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(List.of(0.22f, 0.8f), List.of(1, 42)))
.setUsing("sparse")
.setLimit(20)
.build())
.addPrefetch(PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(List.of(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f)))
.setUsing("dense")
.setLimit(20)
.build())
.setQuery(fusion(Fusion.RRF))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List < PrefetchQuery > {
new() {
Query = new(float, uint)[] {
(0.22f, 1), (0.8f, 42),
},
Using = "sparse",
Limit = 20
},
new() {
Query = new float[] {
0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f
},
Using = "dense",
Limit = 20
}
},
query: Fusion.Rrf
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQuerySparse([]uint32{1, 42}, []float32{0.22, 0.8}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("sparse"),
},
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.45, 0.67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("dense"),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryFusion(qdrant.Fusion_RRF),
})
参数化 RRF
自 v1.16.0 起可用
要更改公式中常数 $k$ 的值,请使用专用的 rrf 查询变体。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": [
// 2+ prefetches here
],
"query": { "rrf": {"k": 60 } }, // <--- parameterized reciprocal rank fusion
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=[
# 2+ prefetches here
],
query=models.RrfQuery(rrf=models.Rrf(k=60)),
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: [
// 2+ prefetches here
],
query: { rrf: { k: 60 } },
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Rrf, PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
// .add_prefetch(...) <┐
// .add_prefetch(...) <┴─ 2+ prefetches here
.query(Query::new_rrf(RrfBuilder::with_k(60))
).await?;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.rrf;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Rrf;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
// .addPrefetch(...) <┐
// .addPrefetch(...) <┴─ 2+ prefetches here
.setQuery(rrf(Rrf.newBuilder().setK(60).build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List<PrefetchQuery>
{
// 2+ prefetches here
},
query: new Rrf
{
K = 60,
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
// 2+ prefetches here
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryRRF(
&qdrant.Rrf{
K: qdrant.PtrOf(uint32(60)),
}),
})
基于分布的分数融合(DBSF)
自 v1.11.0 起可用
DBSF 使用平均值 +/- 3 倍标准差作为限制来标准化每个查询中点的分数,然后将同一查询点在不同查询中的分数相加。多阶段查询
一般来说,更大的向量表示会产生更准确的搜索结果,但计算成本也更高。
将搜索分为两个阶段是缓解这种影响的已知技术:
- 首先,使用更小、更便宜的表示来获取大量候选列表。
- 然后,使用更大、更准确的表示对候选进行重新评分。
有几种方法可以围绕这个想法构建搜索架构:
- 将量化向量作为第一阶段,将全精度向量作为第二阶段。
- 利用俄罗斯套娃表示学习(MRL)生成较短向量的候选,然后用较长的向量进行细化。
- 使用常规密集向量预取候选,然后使用像 ColBERT 这样的多向量模型重新评分。
为了获得最佳效果,Qdrant 提供了一个方便的接口来分阶段执行查询,首先获取粗略结果,然后用更大的向量对其进行细化。
重新评分示例
使用较短的 MRL 字节向量获取 1000 个结果,然后使用完整向量重新评分并获取前 10 个。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
"using": "mrl_byte"
"limit": 1000
},
"query": [0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- full vector
"using": "full",
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[1, 23, 45, 67], # <------------- small byte vector
using="mrl_byte",
limit=1000,
),
query=[0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67], # <-- full vector
using="full",
limit=10,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: {
query: [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
using: 'mrl_byte',
limit: 1000,
},
query: [0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67], // <-- full vector,
using: 'full',
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![1.0, 23.0, 45.0, 67.0]))
.using("mlr_byte")
.limit(1000u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67]))
.using("full")
.limit(10u64)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(1, 23, 45, 67)) // <------------- small byte vector
.setLimit(1000)
.setUsing("mrl_byte")
.build())
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.299f, 0.45f, 0.67f)) // <-- full vector
.setUsing("full")
.setLimit(10)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List<PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Query = new float[] { 1,23, 45, 67 }, // <------------- small byte vector
Using = "mrl_byte",
Limit = 1000
}
},
query: new float[] { 0.01f, 0.299f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, // <-- full vector
usingVector: "full",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{1, 23, 45, 67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("mrl_byte"),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(1000)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("full"),
})
使用默认向量获取 100 个结果,然后使用多向量重新评分以获取前 10 个。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- dense vector
"limit": 100
},
"query": [ // <─┐
[0.1, 0.2, ...], // < │
[0.2, 0.1, ...], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9, ...] // < │
], // <─┘
"using": "colbert",
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[0.01, 0.45, 0.67, 0.53], # <-- dense vector
limit=100,
),
query=[
[0.1, 0.2, 0.32], # <─┐
[0.2, 0.1, 0.52], # < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9, 0.93], # < ┘
],
using="colbert",
limit=10,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: {
query: [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
limit: 100,
},
query: [
[0.1, 0.2], // <─┐
[0.2, 0.1], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9], // < ┘
],
using: 'colbert',
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67]))
.limit(100u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![
vec![0.1, 0.2],
vec![0.2, 0.1],
vec![0.8, 0.9],
]))
.using("colbert")
.limit(10u64)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f)) // <-- dense vector
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
nearest(
new float[][] {
{0.1f, 0.2f}, // <─┐
{0.2f, 0.1f}, // < ├─ multi-vector
{0.8f, 0.9f} // < ┘
}))
.setUsing("colbert")
.setLimit(10)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List <PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Query = new float[] { 0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, // <-- dense vector****
Limit = 100
}
},
query: new float[][] {
[0.1f, 0.2f], // <─┐
[0.2f, 0.1f], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8f, 0.9f] // < ┘
},
usingVector: "colbert",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.45, 0.67}),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(100)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryMulti([][]float32{
{0.1, 0.2},
{0.2, 0.1},
{0.8, 0.9},
}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("colbert"),
})
可以在单个查询中组合所有上述技术。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"prefetch": {
"query": [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------ small byte vector
"using": "mrl_byte"
"limit": 1000
},
"query": [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- full dense vector
"using": "full"
"limit": 100
},
"query": [ // <─┐
[0.1, 0.2, ...], // < │
[0.2, 0.1, ...], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9, ...] // < │
], // <─┘
"using": "colbert",
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[1, 23, 45, 67], # <------ small byte vector
using="mrl_byte",
limit=1000,
),
query=[0.01, 0.45, 0.67], # <-- full dense vector
using="full",
limit=100,
),
query=[
[0.17, 0.23, 0.52], # <─┐
[0.22, 0.11, 0.63], # < ├─ multi-vector
[0.86, 0.93, 0.12], # < ┘
],
using="colbert",
limit=10,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: {
prefetch: {
query: [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
using: 'mrl_byte',
limit: 1000,
},
query: [0.01, 0.45, 0.67], // <-- full dense vector
using: 'full',
limit: 100,
},
query: [
[0.1, 0.2], // <─┐
[0.2, 0.1], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9], // < ┘
],
using: 'colbert',
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![1.0, 23.0, 45.0, 67.0]))
.using("mlr_byte")
.limit(1000u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67]))
.using("full")
.limit(100u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![
vec![0.1, 0.2],
vec![0.2, 0.1],
vec![0.8, 0.9],
]))
.using("colbert")
.limit(10u64)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(1, 23, 45, 67)) // <------------- small byte vector
.setUsing("mrl_byte")
.setLimit(1000)
.build())
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f)) // <-- dense vector
.setUsing("full")
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
nearest(
new float[][] {
{0.1f, 0.2f}, // <─┐
{0.2f, 0.1f}, // < ├─ multi-vector
{0.8f, 0.9f} // < ┘
}))
.setUsing("colbert")
.setLimit(10)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List <PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Prefetch = {
new List <PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Query = new float[] { 1, 23, 45, 67 }, // <------------- small byte vector
Using = "mrl_byte",
Limit = 1000
},
}
},
Query = new float[] {0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f}, // <-- dense vector
Using = "full",
Limit = 100
}
},
query: new float[][] {
[0.1f, 0.2f], // <─┐
[0.2f, 0.1f], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8f, 0.9f] // < ┘
},
usingVector: "colbert",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{1, 23, 45, 67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("mrl_byte"),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(1000)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.45, 0.67}),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(100)),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("full"),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryMulti([][]float32{
{0.1, 0.2},
{0.2, 0.1},
{0.8, 0.9},
}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("colbert"),
})
最大边际相关性(MMR)
从 v1.15.0 版本开始可用
一种提高结果多样性的有用算法是最大边际相关性(MMR)。当数据集对于一个查询包含许多冗余或非常相似的点时,它表现出色。
MMR 迭代地选择候选,从最相关的点(与查询的相似度最高)开始。对于每个下一个点,它选择尚未被选中且与已选点具有最佳相关性与较高分离度组合的点。
$$ MMR = \arg \max_{D_i \in R\setminus S}[\lambda sim(D_i, Q) - (1 - \lambda)\max_{D_j \in S}sim(D_i, D_j)] $$
这在 Qdrant 中作为最近邻查询的一个参数实现。您定义要获取最近候选的向量,以及一个 diversity 参数,该参数控制相关性(0.0)和多样性(1.0)之间的平衡。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"nearest": [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // search vector
"mmr": {
"diversity": 0.5, // 0.0 - relevance; 1.0 - diversity
"candidates_limit": 100 // num of candidates to preselect
}
},
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.NearestQuery(
nearest=[0.01, 0.45, 0.67], # search vector
mmr=models.Mmr(
diversity=0.5, # 0.0 - relevance; 1.0 - diversity
candidates_limit=100, # num of candidates to preselect
)
),
limit=10,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
nearest: [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // search vector
mmr: {
diversity: 0.5, // 0.0 - relevance; 1.0 - diversity
candidates_limit: 100 // num of candidates to preselect
}
},
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest_with_mmr(
vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67], // search vector
MmrBuilder::new()
.diversity(0.5) // 0.0 - relevance; 1.0 - diversity
.candidates_limit(100) // num of candidates to preselect
))
.limit(10)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.VectorInputFactory.vectorInput;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Mmr;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(
nearest(
vectorInput(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f), // <-- search vector
Mmr.newBuilder()
.setDiversity(0.5f) // 0.0 - relevance; 1.0 - diversity
.setCandidatesLimit(100) // num of candidates to preselect
.build()))
.setLimit(10)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: (
new float[] { 0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f },
new Mmr
{
Diversity = 0.5f, // 0.0 - relevance; 1.0 - diversity
CandidatesLimit = 100 // Number of candidates to preselect
}
),
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryMMR(
qdrant.NewVectorInput(0.01, 0.45, 0.67),
&qdrant.Mmr{
Diversity: qdrant.PtrOf(float32(0.5)), // 0.0 - relevance; 1.0 - diversity
CandidatesLimit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint32(100)), // num of candidates to preselect
}),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(10)),
})
注意: 由于 MMR 一次对一个点进行排名,Qdrant 中 MMR 生成的分数是指与查询向量的相似度。这意味着响应不会按分数排序,而是按 MMR 的选择顺序排序。
分数提升
从 v1.14.0 版本开始可用
当在特定应用程序中引入向量搜索时,有时需要考虑业务逻辑来对最终结果列表进行排名。
一个简单的例子是我们自己的文档搜索栏。它包含文档网站每个部分的向量。如果仅通过使用向量执行搜索,所有类型的元素都将被同等视为好的结果。然而,在搜索文档时,我们可以建立一个重要性层次结构:
标题 > 内容 > 片段
解决这个问题的一种方法是根据元素类型对结果进行加权。例如,我们可以为标题和内容分配更高的权重,并保持片段不被提升。
伪代码大概是这样的:
score = score + (is_title * 0.5) + (is_content * 0.25)
Query API 可以使用自定义公式重新评分点。它们可以基于:
- 动态有效载荷值
- 条件
- 预取分数
为了表达公式,语法使用对象来标识每个元素。以文档示例为例,请求将如下所示:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": [0.2, 0.8, ...], // <-- dense vector
"limit": 50
}
"query": {
"formula": {
"sum": [
"$score",
{
"mult": [
0.5,
{
"key": "tag",
"match": { "any": ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"] }
}
]
},
{
"mult": [
0.25,
{
"key": "tag",
"match": { "any": ["p", "li"] }
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import models
tag_boosted = client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[0.2, 0.8, ...], # <-- dense vector
limit=50
),
query=models.FormulaQuery(
formula=models.SumExpression(sum=[
"$score",
models.MultExpression(mult=[0.5, models.FieldCondition(key="tag", match=models.MatchAny(any=["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"]))]),
models.MultExpression(mult=[0.25, models.FieldCondition(key="tag", match=models.MatchAny(any=["p", "li"]))])
]
))
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const tag_boosted = await client.query(collectionName, {
prefetch: {
query: [0.2, 0.8, 0.1, 0.9],
limit: 50
},
query: {
formula: {
sum: [
"$score",
{
mult: [ 0.5, { key: "tag", match: { any: ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"] }} ]
},
{
mult: [ 0.25, { key: "tag", match: { any: ["p", "li"] }} ]
}
]
}
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
Condition, Expression, FormulaBuilder, PrefetchQueryBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
let _tag_boosted = client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67])
.limit(100u64)
)
.query(FormulaBuilder::new(Expression::sum_with([
Expression::score(),
Expression::mult_with([
Expression::constant(0.5),
Expression::condition(Condition::matches("tag", ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"])),
]),
Expression::mult_with([
Expression::constant(0.25),
Expression::condition(Condition::matches("tag", ["p", "li"])),
]),
])))
.limit(10)
).await?;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeywords;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.condition;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.constant;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.mult;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.sum;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.variable;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.formula;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Formula;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.MultExpression;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SumExpression;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f))
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
formula(
Formula.newBuilder()
.setExpression(
sum(
SumExpression.newBuilder()
.addSum(variable("$score"))
.addSum(
mult(
MultExpression.newBuilder()
.addMult(constant(0.5f))
.addMult(
condition(
matchKeywords(
"tag",
List.of("h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"))))
.build()))
.addSum(mult(MultExpression.newBuilder()
.addMult(constant(0.25f))
.addMult(
condition(
matchKeywords(
"tag",
List.of("p", "li"))))
.build()))
.build()))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch:
[
new PrefetchQuery { Query = new float[] { 0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, Limit = 100 },
],
query: new Formula
{
Expression = new SumExpression
{
Sum =
{
"$score",
new MultExpression
{
Mult = { 0.5f, Match("tag", ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"]) },
},
new MultExpression { Mult = { 0.25f, Match("tag", ["p", "li"]) } },
},
},
},
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.01, 0.45, 0.67),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryFormula(&qdrant.Formula{
Expression: qdrant.NewExpressionSum(&qdrant.SumExpression{
Sum: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionVariable("$score"),
qdrant.NewExpressionMult(&qdrant.MultExpression{
Mult: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionConstant(0.5),
qdrant.NewExpressionCondition(qdrant.NewMatchKeywords("tag", "h1", "h2", "h3", "h4")),
},
}),
qdrant.NewExpressionMult(&qdrant.MultExpression{
Mult: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionConstant(0.25),
qdrant.NewExpressionCondition(qdrant.NewMatchKeywords("tag", "p", "li")),
},
}),
},
}),
}),
})
有多种表达式可用,请查看API 文档以获取具体细节。
- constant - 浮点数。例如
0.5。 "$score"- 引用预取中点的分数。这与"$score[0]"相同。"$score[0]","$score[1]","$score[2]", … - 使用多个预取时,可以使用预取数组中的索引来引用特定的预取。- payload key - 任何普通字符串都将引用一个有效载荷键。这使用与其他地方相同的 jsonpath 格式,例如
key或key.subkey。它将尝试从给定键中提取一个数字。 - condition - 过滤条件。如果满足条件,则为
1.0,否则为0.0。 - mult - 乘以表达式数组。
- sum - 对表达式数组求和。
- div - 一个表达式除以另一个表达式。
- abs - 表达式的绝对值。
- pow - 将一个表达式提升到另一个表达式的幂。
- sqrt - 表达式的平方根。
- log10 - 表达式的以 10 为底的对数。
- ln - 表达式的自然对数。
- exp - 表达式的指数函数(
e^x)。 - geo distance - 两个地理点之间的半正矢距离。值需要是
{ "lat": 0.0, "lon": 0.0 }对象。 - decay - 对表达式应用衰减函数,将输出钳制在 0 和 1 之间。可用的衰减函数包括 linear、exponential 和 gaussian。查看更多。
- datetime - 解析日期时间字符串(格式参见此处),并将其用作 POSIX 时间戳,以秒为单位。
- datetime key - 指定有效载荷键包含要解析为 POSIX 秒的日期时间字符串。
可以为找不到变量(来自有效载荷或预取分数)时定义一个默认值。这以变量到值的映射形式给出。如果没有变量,也没有定义默认值,则使用默认值 0.0。
提升离用户更近的点
另一个例子。将分数与结果离用户的距离结合起来。
考虑到每个点都有一个相关的地理位置,我们可以计算点与请求位置之间的距离。
假设我们在预取中具有余弦分数,我们可以使用辅助函数通过衰减函数将地理距离限制在 0 和 1 之间。一旦限制,我们可以将分数和距离相加。伪代码:
score = score + gauss_decay(distance)
在这种情况下,我们使用 gauss_decay 函数。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": { "query": [0.2, 0.8, ...], "limit": 50 },
"query": {
"formula": {
"sum": [
"$score",
{
"gauss_decay": {
"x": {
"geo_distance": {
"origin": { "lat": 52.504043, "lon": 13.393236 }
"to": "geo.location"
}
},
"scale": 5000 // 5km
}
}
]
},
"defaults": { "geo.location": {"lat": 48.137154, "lon": 11.576124} }
}
}
from qdrant_client import models
geo_boosted = client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[0.2, 0.8, ...], # <-- dense vector
limit=50
),
query=models.FormulaQuery(
formula=models.SumExpression(sum=[
"$score",
models.GaussDecayExpression(
gauss_decay=models.DecayParamsExpression(
x=models.GeoDistance(
geo_distance=models.GeoDistanceParams(
origin=models.GeoPoint(
lat=52.504043,
lon=13.393236
), # Berlin
to="geo.location"
)
),
scale=5000 # 5km
)
)
]),
defaults={"geo.location": models.GeoPoint(lat=48.137154, lon=11.576124)} # Munich
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const distance_boosted = await client.query(collectionName, {
prefetch: {
query: [0.2, 0.8, ...],
limit: 50
},
query: {
formula: {
sum: [
"$score",
{
gauss_decay: {
x: {
geo_distance: {
origin: { lat: 52.504043, lon: 13.393236 }, // Berlin
to: "geo.location"
}
},
scale: 5000 // 5km
}
}
]
},
defaults: { "geo.location": { lat: 48.137154, lon: 11.576124 } } // Munich
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
GeoPoint, DecayParamsExpressionBuilder, Expression, FormulaBuilder, PrefetchQueryBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
let _geo_boosted = client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(
PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67])
.limit(100u64),
)
.query(
FormulaBuilder::new(Expression::sum_with([
Expression::score(),
Expression::exp_decay(
DecayParamsExpressionBuilder::new(Expression::geo_distance_with(
// Berlin
GeoPoint { lat: 52.504043, lon: 13.393236 },
"geo.location",
))
.scale(5_000.0),
),
]))
// Munich
.add_default("geo.location", GeoPoint { lat: 48.137154, lon: 11.576124 }),
)
.limit(10),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.expDecay;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.geoDistance;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.sum;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.variable;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.formula;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Common.GeoPoint;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.DecayParamsExpression;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Formula;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.GeoDistance;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SumExpression;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f))
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
formula(
Formula.newBuilder()
.setExpression(
sum(
SumExpression.newBuilder()
.addSum(variable("$score"))
.addSum(
expDecay(
DecayParamsExpression.newBuilder()
.setX(
geoDistance(
GeoDistance.newBuilder()
.setOrigin(
GeoPoint.newBuilder()
.setLat(52.504043)
.setLon(13.393236)
.build())
.setTo("geo.location")
.build()))
.setScale(5000)
.build()))
.build()))
.putDefaults(
"geo.location",
value(
Map.of(
"lat", value(48.137154),
"lon", value(11.576124))))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Expression;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch:
[
new PrefetchQuery { Query = new float[] { 0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, Limit = 100 },
],
query: new Formula
{
Expression = new SumExpression
{
Sum =
{
"$score",
FromExpDecay(
new()
{
X = new GeoDistance
{
Origin = new GeoPoint { Lat = 52.504043, Lon = 13.393236 },
To = "geo.location",
},
Scale = 5000,
}
),
},
},
Defaults =
{
["geo.location"] = new Dictionary<string, Value>
{
["lat"] = 48.137154,
["lon"] = 11.576124,
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.8),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryFormula(&qdrant.Formula{
Expression: qdrant.NewExpressionSum(&qdrant.SumExpression{
Sum: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionVariable("$score"),
qdrant.NewExpressionExpDecay(&qdrant.DecayParamsExpression{
X: qdrant.NewExpressionGeoDistance(&qdrant.GeoDistance{
Origin: &qdrant.GeoPoint{
Lat: 52.504043,
Lon: 13.393236,
},
To: "geo.location",
}),
}),
},
}),
Defaults: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"geo.location": map[string]any{
"lat": 48.137154,
"lon": 11.576124,
},
}),
}),
})
基于时间的分数提升
或者将分数与结果的“新鲜度”信息结合起来。它适用于(新闻)文章以及通常许多其他不同类型的搜索(想想您在应用程序中使用的“最新”过滤器)。
要实现基于时间的分数提升,您需要每个点在其有效载荷中都有一个日期时间字段,例如,项目上传或上次更新的时间。然后我们可以计算此有效载荷值与当前时间(我们的 target)之间的时间差,以秒为单位。
使用指数衰减函数,非常适合时间用例,因为新鲜度是一个很快失去的品质,我们可以将这个时间差转换为 0 到 1 之间的值,然后将其添加到原始分数中以优先处理新鲜结果。
score = score + exp_decay(current_time - point_time)
这就是一个应用程序的样子,在 1 天后,结果开始只有一半相关(所以得到 0.5 分)。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": [0.2, 0.8, ...], // <-- dense vector
"limit": 50
},
"query": {
"formula": {
"sum": [
"$score", // the final score = score + exp_decay(target_time - x_time)
{
"exp_decay": {
"x": {
"datetime_key": "update_time" // payload key
},
"target": {
"datetime": "YYYY-MM-DDT00:00:00Z" // current datetime
},
"scale": 86400, // 1 day in seconds
"midpoint": 0.5 // if item's "update_time" is more than 1 day apart from current datetime, relevance score is less than 0.5
}
}
]
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import models
time_boosted = client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[0.2, 0.8, ...], # <-- dense vector
limit=50
),
query=models.FormulaQuery(
formula=models.SumExpression(
sum=[
"$score", # the final score = score + exp_decay(target_time - x_time)
models.ExpDecayExpression(
exp_decay=models.DecayParamsExpression(
x=models.DatetimeKeyExpression(
datetime_key="upload_time" # payload key
),
target=models.DatetimeExpression(
datetime="YYYY-MM-DDT00:00:00Z" # current datetime
),
scale=86400, # 1 day in seconds
midpoint=0.5 # if item's "update_time" is more than 1 day apart from current datetime, relevance score is less than 0.5
)
)
]
)
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const time_boosted = await client.query(collectionName, {
prefetch: {
query: [0.2, 0.8, ...], // <-- dense vector
limit: 50
},
query: {
formula: {
sum: [ // the final score = score + exp_decay(target_time - x_time)
"$score",
{
exp_decay: {
x: {
datetime_key: "update_time" // payload key
},
target: {
datetime: "YYYY-MM-DDT00:00:00Z" // current datetime
},
midpoint: 0.5,
scale: 86400 // 1 day in seconds
}
}
]
}
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
DecayParamsExpressionBuilder, Expression, FormulaBuilder, PrefetchQueryBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
let _geo_boosted = client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(
PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(vec![0.2, 0.8, .., ..]) // <-- dense vector
.limit(50u64),
)
.query(
FormulaBuilder::new(Expression::sum_with([ // the final score = score + exp_decay(target_time - x_time)
Expression::score(),
Expression::exp_decay(
DecayParamsExpressionBuilder::new(Expression::datetime_key("update_time")) // payload key
.target(Expression::datetime("YYYY-MM-DDT00:00:00Z"))
.midpoint(0.5)
.scale(86400.0), // 1 day in seconds
),
]))
)
)
.await?;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.DecayParamsExpression;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Formula;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.ScoredPoint;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SumExpression;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.datetime;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.datetimeKey;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.expDecay;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.sum;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.variable;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.formula;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
List<ScoredPoint> time_boosted = client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName({collection_name})
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.8f, .., ..)) // <-- dense vector
.setLimit(50)
.build())
.setQuery(
formula(
Formula.newBuilder()
.setExpression(
sum( // the final score = score + exp_decay(target_time - x_time)
SumExpression.newBuilder()
.addSum(variable("$score"))
.addSum(
expDecay(
DecayParamsExpression.newBuilder()
.setX(
datetimeKey("update_time")) // payload key
.setTarget(
datetime("YYYY-MM-DDT00:00:00Z")) // current datetime
.setMidpoint(0.5f)
.setScale(86400) // 1 day in seconds
.build()))
.build()))
.build()))
.build()
).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch:
[
new PrefetchQuery { Query = new float[] { 0.2f, 0.8f, ..., .. }, Limit = 50 }, // <-- dense vector
],
query: new Formula
{
Expression = new SumExpression
{
Sum = // the final score = score + exp_decay(target_time - x_time)
{
"$score",
Expression.FromExpDecay(
new()
{
X = Expression.FromDateTimeKey("update_time"), // payload key
Target = Expression.FromDateTime("YYYY-MM-DDT00:00:00Z"), // current datetime
Midpoint = 0.5f,
Scale = 86400 // 1 day in seconds
}
)
}
}
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.8, .., ...), // <-- dense vector
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(50)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryFormula(&qdrant.Formula{
Expression: qdrant.NewExpressionSum(&qdrant.SumExpression{
Sum: []*qdrant.Expression{ // the final score = score + exp_decay(target_time - x_time)
qdrant.NewExpressionVariable("$score"),
qdrant.NewExpressionExpDecay(&qdrant.DecayParamsExpression{
X: qdrant.NewExpressionDatetimeKey("update_time"), // payload key
Target: qdrant.NewExpressionDatetime("YYYY-MM-DDT00:00:00Z"), // current datetime
Scale: qdrant.PtrOf(float32(86400)), // 1 day in seconds
Midpoint: qdrant.PtrOf(float32(0.5)),
}),
},
}),
}),
})
对于所有衰减函数,都有这些可用参数:
| 参数 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
x | 不适用 | 要衰减的值 |
target | 0.0 | 衰减达到峰值时的值。对于距离,通常设置为 0.0,但可以设置为任何值。 |
scale | 1.0 | 衰减函数等于 midpoint 时的值。这以 x 单位表示,例如,如果 x 以米为单位,scale 为 5000 意味着 5 公里。必须是非零正数。 |
midpoint | 0.5 | 当 x 等于 target ± scale 时,输出为 midpoint。必须在 (0.0, 1.0) 范围内,不包括两端。 |
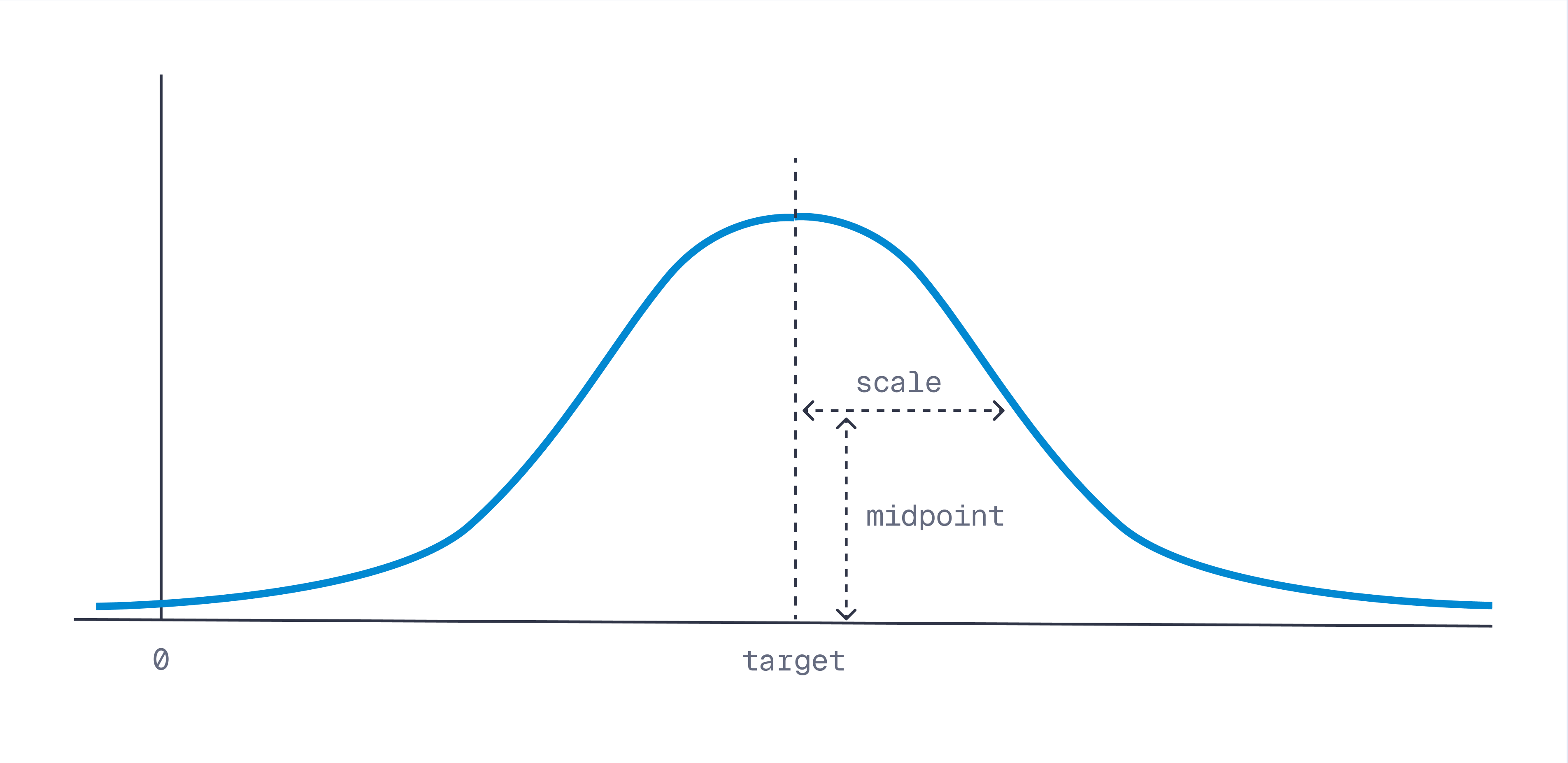
每个衰减函数公式如下:
| 衰减函数 | 颜色 | 范围 | 公式 |
|---|---|---|---|
lin_decay | 绿色 | [0, 1] | $\text{lin_decay}(x) = \max\left(0,\ -\frac{(1-m_{idpoint})}{s_{cale}}\cdot {abs}(x-t_{arget})+1\right)$ |
exp_decay | 红色 | (0, 1] | $\text{exp_decay}(x) = \exp\left(\frac{\ln(m_{idpoint})}{s_{cale}}\cdot {abs}(x-t_{arget})\right)$ |
gauss_decay | 紫色 | (0, 1] | $\text{gauss_decay}(x) = \exp\left(\frac{\ln(m_{idpoint})}{s_{cale}^{2}}\cdot (x-t_{arget})^{2}\right)$ |
分组
自 v1.11.0 起可用
可以将结果按特定字段分组。当同一项目有多个点,并且您希望避免结果中同一项目的冗余时,这很有用。
REST API (Schema)
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query/groups
{
// Same as in the regular query API
"query": [1.1],
// Grouping parameters
"group_by": "document_id", // Path of the field to group by
"limit": 4, // Max amount of groups
"group_size": 2 // Max amount of points per group
}
client.query_points_groups(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
# Same as in the regular query_points() API
query=[1.1],
# Grouping parameters
group_by="document_id", # Path of the field to group by
limit=4, # Max amount of groups
group_size=2, # Max amount of points per group
)
client.queryGroups("{collection_name}", {
query: [1.1],
group_by: "document_id",
limit: 4,
group_size: 2,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointGroupsBuilder;
client
.query_groups(
QueryPointGroupsBuilder::new("{collection_name}", "document_id")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.group_size(2u64)
.with_payload(true)
.with_vectors(true)
.limit(4u64),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SearchPointGroups;
client.queryGroupsAsync(
QueryPointGroups.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setGroupBy("document_id")
.setLimit(4)
.setGroupSize(2)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryGroupsAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
groupBy: "document_id",
limit: 4,
groupSize: 2
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.QueryGroups(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPointGroups{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
GroupBy: "document_id",
GroupSize: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(2)),
})
