相似度搜索
搜索最近的向量是许多表征学习应用的核心。现代神经网络经过训练,将对象转换为向量,使得现实世界中接近的对象在向量空间中也显得接近。例如,具有相似含义的文本、视觉上相似的图片或同一类型的歌曲。
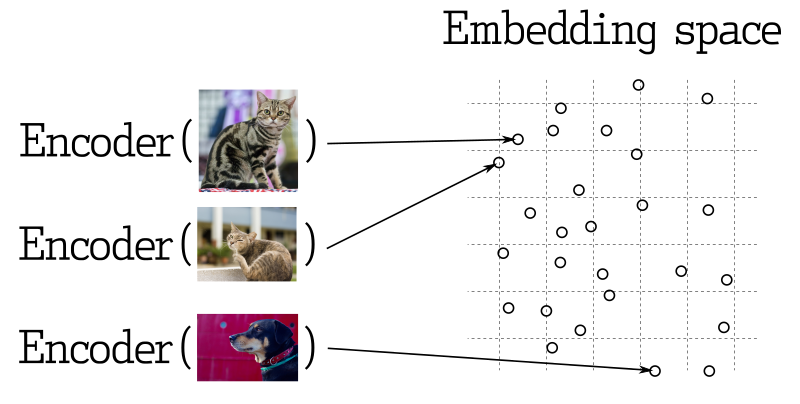
向量相似度的工作原理如下
查询 API
v1.10.0 版本起可用
Qdrant 提供了一个单一接口用于所有类型的搜索和探索请求 - Query API。以下是您可以使用 Qdrant 中的 Query API 执行的查询类型参考列表
根据 query 参数的不同,Qdrant 可能会为搜索选择不同的策略。
| 最近邻搜索 | 向量相似度搜索,也称为 k-NN |
| 按 ID 搜索 | 通过已存储的向量进行搜索 - 跳过嵌入模型推理 |
| 推荐 | 提供正面和负面示例 |
| 发现式搜索 | 使用上下文作为一次性训练集来指导搜索 |
| 滚动 | 获取所有点,可带过滤 |
| 分组 | 按特定字段对结果进行分组 |
| 按…排序 | 按 payload 键对点进行排序 |
| 混合搜索 | 组合多个查询以获得更好的结果 |
| 多阶段搜索 | 优化大型嵌入的性能 |
| 随机采样 | 从集合中获取随机点 |
最近邻搜索
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7] // <--- Dense vector
}
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7], # <--- Dense vector
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7], // <--- Dense vector
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Condition, Filter, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7]))
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collectionName}")
.setQuery(nearest(List.of(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f)))
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f }
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
})
按 ID 搜索
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": "43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04" // <--- point id
}
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query="43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04", # <--- point id
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: '43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04', // <--- point id
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Condition, Filter, PointId, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(PointId::new("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")))
)
.await?;
import java.util.UUID;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collectionName}")
.setQuery(nearest(UUID.fromString("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")))
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: Guid.Parse("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryID(qdrant.NewID("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")),
})
距离度量
有许多方法可以估算向量之间的相似度。在 Qdrant 中,这些方法被称为距离度量。度量的选择取决于获得的向量,特别是取决于神经网络编码器的训练方法。
Qdrant 支持这些最常见的距离度量类型
- 点积:
Dot- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product - 余弦相似度:
Cosine- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosine_similarity - 欧几里得距离:
Euclid- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance - 曼哈顿距离:
Manhattan*- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxicab_geometry *v1.7 版本起可用
相似度学习模型中最常用的度量是余弦度量。
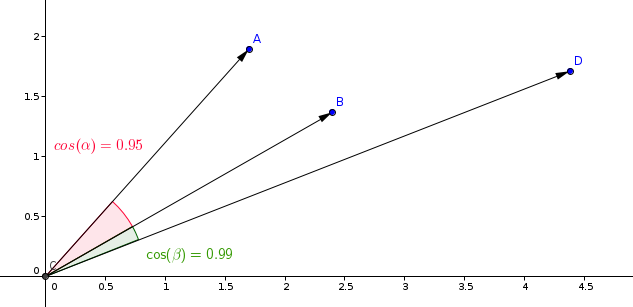
Qdrant 分两步计算这个度量,从而实现更高的搜索速度。第一步是在将向量添加到集合时对其进行归一化。每个向量只发生一次。
第二步是向量的比较。在这种情况下,它等同于点积——由于 SIMD,这是一个非常快的操作。
根据查询配置的不同,Qdrant 可能会为搜索选择不同的策略。请在查询规划部分阅读更多内容。
搜索 API
我们来看一个搜索查询的例子。
REST API - API 模式定义可在此处获得
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.79],
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"value": "London"
}
}
]
},
"params": {
"hnsw_ef": 128,
"exact": false
},
"limit": 3
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
query_filter=models.Filter(
must=[
models.FieldCondition(
key="city",
match=models.MatchValue(
value="London",
),
)
]
),
search_params=models.SearchParams(hnsw_ef=128, exact=False),
limit=3,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
filter: {
must: [
{
key: "city",
match: {
value: "London",
},
},
],
},
params: {
hnsw_ef: 128,
exact: false,
},
limit: 3,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Condition, Filter, QueryPointsBuilder, SearchParamsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.limit(3)
.filter(Filter::must([Condition::matches(
"city",
"London".to_string(),
)]))
.params(SearchParamsBuilder::default().hnsw_ef(128).exact(false)),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeyword;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Filter;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SearchParams;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setFilter(Filter.newBuilder().addMust(matchKeyword("city", "London")).build())
.setParams(SearchParams.newBuilder().setExact(false).setHnswEf(128).build())
.setLimit(3)
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
filter: MatchKeyword("city", "London"),
searchParams: new SearchParams { Exact = false, HnswEf = 128 },
limit: 3
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
Filter: &qdrant.Filter{
Must: []*qdrant.Condition{
qdrant.NewMatch("city", "London"),
},
},
Params: &qdrant.SearchParams{
Exact: qdrant.PtrOf(false),
HnswEf: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(128)),
},
})
在此示例中,我们正在寻找与向量 [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7] 相似的向量。参数 limit(或其别名 top)指定了我们希望检索到的最相似结果的数量。
键 params 下的值指定了搜索的自定义参数。目前,它可以是
hnsw_ef- 指定 HNSW 算法ef参数的值。exact- 不使用近似搜索 (ANN) 的选项。如果设置为 true,搜索可能会运行很长时间,因为它会执行完全扫描以检索精确结果。indexed_only- 使用此选项,您可以禁用在尚未构建向量索引的 segment 中的搜索。如果您想在集合更新的同时最大限度地减少对搜索性能的影响,这可能会很有用。如果在集合尚未完全索引的情况下使用此选项,可能会导致部分结果,请仅在您的用例可以接受最终一致性时考虑使用它。
由于指定了 filter 参数,搜索仅在满足过滤条件的点中执行。请参阅过滤部分,了解可能的过滤器及其工作的详细信息。
此 API 的示例结果将是
{
"result": [
{ "id": 10, "score": 0.81 },
{ "id": 14, "score": 0.75 },
{ "id": 11, "score": 0.73 }
],
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}
result 包含按 score 排序的找到的点 ID 列表。
请注意,默认情况下,这些结果中缺少 payload 和向量数据。请参阅结果中的 payload 和向量,了解如何包含它们。
如果集合是使用多个向量创建的,则应提供用于搜索的向量名称
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"using": "image",
"limit": 3
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
using="image",
limit=3,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
using: "image",
limit: 3,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointsBuilder;
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.limit(3)
.using("image"),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setUsing("image")
.setLimit(3)
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
usingVector: "image",
limit: 3
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("image"),
})
搜索仅处理名称相同的向量。
如果集合是使用稀疏向量创建的,则应提供用于搜索的稀疏向量名称
您仍然可以将 payload 过滤和搜索 API 的其他功能用于稀疏向量。
然而,密集向量搜索和稀疏向量搜索之间存在重要差异
| 索引 | 稀疏查询 | 密集查询 |
|---|---|---|
| 评分度量 | 默认为 Dot product,无需指定 | Distance 支持 Dot、Cosine 等度量 |
| 搜索类型 | 在 Qdrant 中始终精确 | HNSW 是近似 NN |
| 返回行为 | 仅返回与查询向量在相同索引中具有非零值的向量 | 返回 limit 个向量 |
通常,搜索的速度与查询向量中非零值的数量成正比。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"indices": [1, 3, 5, 7],
"values": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]
},
"using": "text"
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
result = client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.SparseVector(indices=[1, 3, 5, 7], values=[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]),
using="text",
).points
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
indices: [1, 3, 5, 7],
values: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]
},
using: "text",
limit: 3,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointsBuilder;
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![(1, 0.2), (3, 0.1), (5, 0.9), (7, 0.7)])
.limit(10)
.using("text"),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setUsing("text")
.setQuery(nearest(List.of(0.1f, 0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f), List.of(1, 3, 5, 7)))
.setLimit(3)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new (float, uint)[] {(0.1f, 1), (0.2f, 3), (0.3f, 5), (0.4f, 7)},
usingVector: "text",
limit: 3
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuerySparse(
[]uint32{1, 3, 5, 7},
[]float32{0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("text"),
})
按分数过滤结果
除了 payload 过滤之外,过滤掉相似度得分低的结果也很有用。例如,如果您知道模型的最小可接受分数,并且不希望任何相似度低于该阈值的结果。在这种情况下,您可以使用搜索查询的 score_threshold 参数。它将排除所有得分差于给定阈值的结果。
结果中的 Payload 和向量
默认情况下,检索方法不返回任何存储的信息,如 payload 和向量。额外的参数 with_vectors 和 with_payload 改变此行为。
示例
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"with_vectors": true,
"with_payload": true
}
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_vectors=True,
with_payload=True,
)
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_vector: true,
with_payload: true,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointsBuilder;
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.limit(3)
.with_payload(true)
.with_vectors(true),
)
.await?;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.WithVectorsSelectorFactory;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.WithPayloadSelectorFactory.enable;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setWithPayload(enable(true))
.setWithVectors(WithVectorsSelectorFactory.enable(true))
.setLimit(3)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
payloadSelector: true,
vectorsSelector: true,
limit: 3
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
WithPayload: qdrant.NewWithPayload(true),
WithVectors: qdrant.NewWithVectors(true),
})
您可以使用 with_payload 来限定或过滤特定的 payload 子集。您甚至可以指定要包含的项数组,例如 city、village 和 town
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"with_payload": ["city", "village", "town"]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_payload=["city", "village", "town"],
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_payload: ["city", "village", "town"],
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{with_payload_selector::SelectorOptions, QueryPointsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.limit(3)
.with_payload(SelectorOptions::Include(
vec![
"city".to_string(),
"village".to_string(),
"town".to_string(),
]
.into(),
))
.with_vectors(true),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.WithPayloadSelectorFactory.include;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setWithPayload(include(List.of("city", "village", "town")))
.setLimit(3)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
payloadSelector: new WithPayloadSelector
{
Include = new PayloadIncludeSelector
{
Fields = { new string[] { "city", "village", "town" } }
}
},
limit: 3
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
WithPayload: qdrant.NewWithPayloadInclude("city", "village", "town"),
})
或者显式使用 include 或 exclude。例如,要排除 city
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"with_payload": {
"exclude": ["city"]
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_payload=models.PayloadSelectorExclude(
exclude=["city"],
),
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_payload: {
exclude: ["city"],
},
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{with_payload_selector::SelectorOptions, QueryPointsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.limit(3)
.with_payload(SelectorOptions::Exclude(vec!["city".to_string()].into()))
.with_vectors(true),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.WithPayloadSelectorFactory.exclude;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setWithPayload(exclude(List.of("city")))
.setLimit(3)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
payloadSelector: new WithPayloadSelector
{
Exclude = new PayloadExcludeSelector { Fields = { new string[] { "city" } } }
},
limit: 3
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
WithPayload: qdrant.NewWithPayloadExclude("city"),
})
可以使用点符号定位嵌套字段
payload.nested_field- 对于嵌套字段payload.nested_array[].sub_field- 用于投影数组内的嵌套字段
目前不支持通过索引访问数组元素。
批量搜索 API
批量搜索 API 允许通过一个请求执行多个搜索请求。
其语义直观,n 个批量搜索请求等同于 n 个单独的搜索请求。
这种方法有几个优点。逻辑上,需要更少的网络连接,这本身非常有益。
更重要的是,批量请求将通过查询规划器高效处理,如果它们具有相同的 filter,查询规划器可以检测并优化请求。
这对于非平凡过滤器可以极大地影响延迟,因为中间结果可以在请求之间共享。
要使用它,只需将您的搜索请求打包在一起即可。搜索请求的所有常规属性当然都可用。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query/batch
{
"searches": [
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"value": "London"
}
}
]
},
"limit": 3
},
{
"query": [0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3],
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"value": "London"
}
}
]
},
"limit": 3
}
]
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
filter_ = models.Filter(
must=[
models.FieldCondition(
key="city",
match=models.MatchValue(
value="London",
),
)
]
)
search_queries = [
models.QueryRequest(query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7], filter=filter_, limit=3),
models.QueryRequest(query=[0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3], filter=filter_, limit=3),
]
client.query_batch_points(collection_name="{collection_name}", requests=search_queries)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const filter = {
must: [
{
key: "city",
match: {
value: "London",
},
},
],
};
const searches = [
{
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
filter,
limit: 3,
},
{
query: [0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3],
filter,
limit: 3,
},
];
client.queryBatch("{collection_name}", {
searches,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Condition, Filter, QueryBatchPointsBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
let filter = Filter::must([Condition::matches("city", "London".to_string())]);
let searches = vec![
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4])
.limit(3)
.filter(filter.clone())
.build(),
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3])
.limit(3)
.filter(filter)
.build(),
];
client
.query_batch(QueryBatchPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}", searches))
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Filter;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeyword;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
Filter filter = Filter.newBuilder().addMust(matchKeyword("city", "London")).build();
List<QueryPoints> searches = List.of(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setFilter(filter)
.setLimit(3)
.build(),
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setFilter(filter)
.setLimit(3)
.build());
client.queryBatchAsync("{collection_name}", searches).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
var filter = MatchKeyword("city", "London");
var queries = new List<QueryPoints>
{
new()
{
CollectionName = "{collection_name}",
Query = new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
Filter = filter,
Limit = 3
},
new()
{
CollectionName = "{collection_name}",
Query = new float[] { 0.5f, 0.3f, 0.2f, 0.3f },
Filter = filter,
Limit = 3
}
};
await client.QueryBatchAsync(collectionName: "{collection_name}", queries: queries);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
filter := qdrant.Filter{
Must: []*qdrant.Condition{
qdrant.NewMatch("city", "London"),
},
}
client.QueryBatch(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryBatchPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
QueryPoints: []*qdrant.QueryPoints{
{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
Filter: &filter,
},
{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3),
Filter: &filter,
},
},
})
此 API 的结果包含每个搜索请求的一个数组。
{
"result": [
[
{ "id": 10, "score": 0.81 },
{ "id": 14, "score": 0.75 },
{ "id": 11, "score": 0.73 }
],
[
{ "id": 1, "score": 0.92 },
{ "id": 3, "score": 0.89 },
{ "id": 9, "score": 0.75 }
]
],
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}
按 ID 查询
无论何时您需要使用向量作为输入,您都可以始终使用点 ID 来代替。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": "43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04" // <--- point id
}
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query="43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04", # <--- point id
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: '43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04', // <--- point id
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Condition, Filter, PointId, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest(PointId::new("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")))
)
.await?;
import java.util.UUID;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collectionName}")
.setQuery(nearest(UUID.fromString("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")))
.build()).get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: Guid.Parse("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryID(qdrant.NewID("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")),
})
上面的示例将从具有此 ID 的点中获取默认向量,并将其用作查询向量。
如果同时指定了 using 参数,Qdrant 将使用具有该名称的向量。
也可以通过设置 lookup_from 参数来引用不同集合中的 ID。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": "43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04", // <--- point id
"using": "512d-vector"
"lookup_from": {
"collection": "another_collection", // <--- other collection name
"vector": "image-512" // <--- vector name in the other collection
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query="43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04", # <--- point id
using="512d-vector",
lookup_from=models.LookupLocation(
collection="another_collection", # <--- other collection name
vector="image-512", # <--- vector name in the other collection
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: '43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04', // <--- point id
using: '512d-vector',
lookup_from: {
collection: 'another_collection', // <--- other collection name
vector: 'image-512', // <--- vector name in the other collection
}
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{LookupLocationBuilder, PointId, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_nearest("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04"))
.using("512d-vector")
.lookup_from(
LookupLocationBuilder::new("another_collection")
.vector_name("image-512")
)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.LookupLocation;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import java.util.UUID;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(UUID.fromString("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")))
.setUsing("512d-vector")
.setLookupFrom(
LookupLocation.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("another_collection")
.setVectorName("image-512")
.build())
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: Guid.Parse("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04"), // <--- point id
usingVector: "512d-vector",
lookupFrom: new() {
CollectionName = "another_collection", // <--- other collection name
VectorName = "image-512" // <--- vector name in the other collection
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQueryID(qdrant.NewID("43cf51e2-8777-4f52-bc74-c2cbde0c8b04")),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("512d-vector"),
LookupFrom: &qdrant.LookupLocation{
CollectionName: "another_collection",
VectorName: qdrant.PtrOf("image-512"),
},
})
在上述情况下,Qdrant 将从集合 another_collection 中指定点 ID 的 "image-512" 向量中获取。
分页
搜索和推荐 API 允许跳过搜索的前 N 个结果,并仅返回从指定偏移量开始的结果
示例
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"with_vectors": true,
"with_payload": true,
"limit": 10,
"offset": 100
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
client = QdrantClient(url="https://:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=[0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_vectors=True,
with_payload=True,
limit=10,
offset=100,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
with_vector: true,
with_payload: true,
limit: 10,
offset: 100,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointsBuilder;
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.with_payload(true)
.with_vectors(true)
.limit(10)
.offset(100),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.WithVectorsSelectorFactory;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.WithPayloadSelectorFactory.enable;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setWithPayload(enable(true))
.setWithVectors(WithVectorsSelectorFactory.enable(true))
.setLimit(10)
.setOffset(100)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
payloadSelector: true,
vectorsSelector: true,
limit: 10,
offset: 100
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
WithPayload: qdrant.NewWithPayload(true),
WithVectors: qdrant.NewWithVectors(true),
Offset: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(100)),
})
相当于检索每页 10 条记录的第 11 页。
基于向量的检索,特别是 HNSW 索引,并非设计用于分页。不可能在不先检索前 N 个向量的情况下检索第 N 个最近的向量。
然而,使用偏移量参数通过减少网络流量和访问存储的次数来节省资源。
使用 offset 参数需要内部检索 offset + limit 个点,但只从存储中访问实际将返回的那些点的 payload 和向量。
分组 API
可以按特定字段对结果进行分组。当同一项有多个点,并且您想避免结果中出现相同的项时,这很有用。
例如,如果您有一个大型文档被分割成多个块,并且您想按文档进行搜索或推荐,您可以按文档 ID 对结果进行分组。
考虑拥有以下 payload 的点
[
{
"id": 0,
"payload": {
"chunk_part": 0,
"document_id": "a"
},
"vector": [0.91]
},
{
"id": 1,
"payload": {
"chunk_part": 1,
"document_id": ["a", "b"]
},
"vector": [0.8]
},
{
"id": 2,
"payload": {
"chunk_part": 2,
"document_id": "a"
},
"vector": [0.2]
},
{
"id": 3,
"payload": {
"chunk_part": 0,
"document_id": 123
},
"vector": [0.79]
},
{
"id": 4,
"payload": {
"chunk_part": 1,
"document_id": 123
},
"vector": [0.75]
},
{
"id": 5,
"payload": {
"chunk_part": 0,
"document_id": -10
},
"vector": [0.6]
}
]
使用 groups API,您可以获得每个文档的最佳 N 个点,前提是点的 payload 包含文档 ID。当然,有时由于点不足或与查询的距离较大,无法满足最佳 N 个点的要求。在任何情况下,group_size 都是一个尽力而为的参数,类似于 limit 参数。
搜索分组
REST API (Schema)
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query/groups
{
// Same as in the regular query API
"query": [1.1],
// Grouping parameters
"group_by": "document_id", // Path of the field to group by
"limit": 4, // Max amount of groups
"group_size": 2 // Max amount of points per group
}
client.query_points_groups(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
# Same as in the regular query_points() API
query=[1.1],
# Grouping parameters
group_by="document_id", # Path of the field to group by
limit=4, # Max amount of groups
group_size=2, # Max amount of points per group
)
client.queryGroups("{collection_name}", {
query: [1.1],
group_by: "document_id",
limit: 4,
group_size: 2,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointGroupsBuilder;
client
.query_groups(
QueryPointGroupsBuilder::new("{collection_name}", "document_id")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.group_size(2u64)
.with_payload(true)
.with_vectors(true)
.limit(4u64),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SearchPointGroups;
client.queryGroupsAsync(
QueryPointGroups.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setGroupBy("document_id")
.setLimit(4)
.setGroupSize(2)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryGroupsAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
groupBy: "document_id",
limit: 4,
groupSize: 2
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.QueryGroups(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPointGroups{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
GroupBy: "document_id",
GroupSize: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(2)),
})
groups 调用的输出如下所示
{
"result": {
"groups": [
{
"id": "a",
"hits": [
{ "id": 0, "score": 0.91 },
{ "id": 1, "score": 0.85 }
]
},
{
"id": "b",
"hits": [
{ "id": 1, "score": 0.85 }
]
},
{
"id": 123,
"hits": [
{ "id": 3, "score": 0.79 },
{ "id": 4, "score": 0.75 }
]
},
{
"id": -10,
"hits": [
{ "id": 5, "score": 0.6 }
]
}
]
},
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}
组按组中得分最高的点的分数排序。每个组内的点也已排序。
如果点的 group_by 字段是一个数组(例如 "document_id": ["a", "b"]),则该点可以包含在多个组中(例如 "document_id": "a" 和 document_id: "b")。
限制:
分组中的查找
同一项的部分存在多个点通常会在存储的数据中引入冗余。如果点共享的信息很小,这可能没有问题,但如果 payload 很大,则会成为问题,因为它会将存储点所需的存储空间乘以每组点的数量。
使用分组时优化存储的一种方法是将具有相同组 ID 的点共享的信息存储在另一个集合的单个点中。然后,在使用groups API 时,添加 with_lookup 参数将这些点的信息带入每个组中。
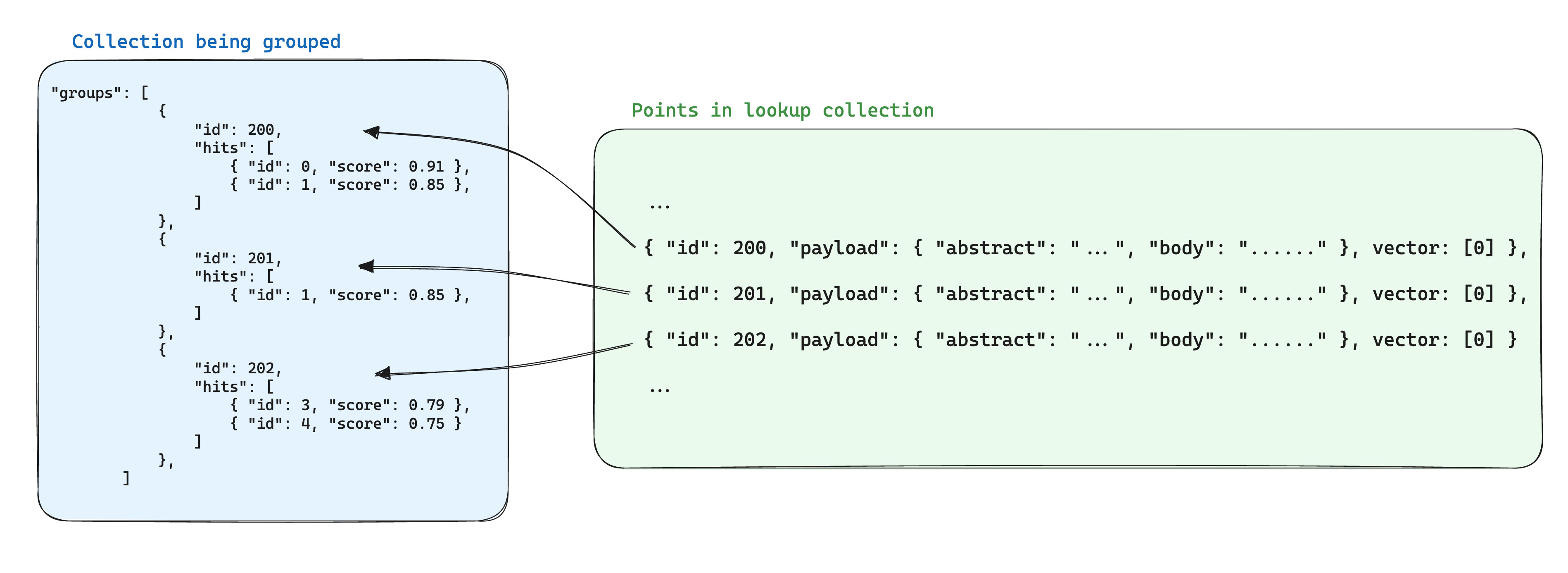
这样做还有一个额外的好处,即当组中点共享的信息发生变化时,只需更新单个点。
例如,如果您有一个文档集合,您可能希望将其分块,并将块的点存储在一个单独的集合中,确保在块点的 payload 中存储它所属文档的点 ID。
在这种情况下,要将文档信息带入按文档 ID 分组的块中,您可以使用 with_lookup 参数
POST /collections/chunks/points/query/groups
{
// Same as in the regular query API
"query": [1.1],
// Grouping parameters
"group_by": "document_id",
"limit": 2,
"group_size": 2,
// Lookup parameters
"with_lookup": {
// Name of the collection to look up points in
"collection": "documents",
// Options for specifying what to bring from the payload
// of the looked up point, true by default
"with_payload": ["title", "text"],
// Options for specifying what to bring from the vector(s)
// of the looked up point, true by default
"with_vectors": false
}
}
client.query_points_groups(
collection_name="chunks",
# Same as in the regular search() API
query=[1.1],
# Grouping parameters
group_by="document_id", # Path of the field to group by
limit=2, # Max amount of groups
group_size=2, # Max amount of points per group
# Lookup parameters
with_lookup=models.WithLookup(
# Name of the collection to look up points in
collection="documents",
# Options for specifying what to bring from the payload
# of the looked up point, True by default
with_payload=["title", "text"],
# Options for specifying what to bring from the vector(s)
# of the looked up point, True by default
with_vectors=False,
),
)
client.queryGroups("{collection_name}", {
query: [1.1],
group_by: "document_id",
limit: 2,
group_size: 2,
with_lookup: {
collection: "documents",
with_payload: ["title", "text"],
with_vectors: false,
},
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{with_payload_selector::SelectorOptions, QueryPointGroupsBuilder, WithLookupBuilder};
client
.query_groups(
QueryPointGroupsBuilder::new("{collection_name}", "document_id")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.limit(2u64)
.limit(2u64)
.with_lookup(
WithLookupBuilder::new("documents")
.with_payload(SelectorOptions::Include(
vec!["title".to_string(), "text".to_string()].into(),
))
.with_vectors(false),
),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPointGroups;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.WithLookup;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.WithVectorsSelectorFactory.enable;
import static io.qdrant.client.WithPayloadSelectorFactory.include;
client.queryGroupsAsync(
QueryPointGroups.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setGroupBy("document_id")
.setLimit(2)
.setGroupSize(2)
.setWithLookup(
WithLookup.newBuilder()
.setCollection("documents")
.setWithPayload(include(List.of("title", "text")))
.setWithVectors(enable(false))
.build())
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.SearchGroupsAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
vector: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f},
groupBy: "document_id",
limit: 2,
groupSize: 2,
withLookup: new WithLookup
{
Collection = "documents",
WithPayload = new WithPayloadSelector
{
Include = new PayloadIncludeSelector { Fields = { new string[] { "title", "text" } } }
},
WithVectors = false
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.QueryGroups(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPointGroups{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
GroupBy: "document_id",
GroupSize: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(2)),
WithLookup: &qdrant.WithLookup{
Collection: "documents",
WithPayload: qdrant.NewWithPayloadInclude("title", "text"),
},
})
对于 with_lookup 参数,您还可以使用简写 with_lookup="documents" 来带入整个 payload 和向量,而无需显式指定。
查找的结果将显示在每个组的 lookup 下。
{
"result": {
"groups": [
{
"id": 1,
"hits": [
{ "id": 0, "score": 0.91 },
{ "id": 1, "score": 0.85 }
],
"lookup": {
"id": 1,
"payload": {
"title": "Document A",
"text": "This is document A"
}
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"hits": [
{ "id": 1, "score": 0.85 }
],
"lookup": {
"id": 2,
"payload": {
"title": "Document B",
"text": "This is document B"
}
}
}
]
},
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}
由于查找是通过直接匹配点 ID 来完成的,因此查找集合必须预先填充点,这些点的 id 与您的主集合中的 group_by 值(例如,document_id)匹配。
任何在查找集合中不是现有(且有效)点 ID 的组 ID 将被忽略,并且 lookup 字段将为空。
随机采样
v1.11.0 版本起可用
在某些情况下,检索集合中点的随机样本可能很有用。这可用于调试、测试或提供探索入口点。
随机采样 API 是通用查询 API 的一部分,可以像常规搜索 API 一样使用。
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"query": {
"sample": "random"
}
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
sampled = client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
query=models.SampleQuery(sample=models.Sample.RANDOM)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const sampled = await client.query("{collection_name}", {
query: {
sample: "random",
},
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("https://:6334").build()?;
let sampled = client
.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.query(Query::new_sample(Sample::Random))
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.sample;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Sample;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(sample(Sample.Random))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(collectionName: "{collection_name}", query: Sample.Random);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.QueryGroups(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPointGroups{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuerySample(qdrant.Sample_Random),
})
查询规划
根据搜索中使用的过滤器,存在几种可能的查询执行方案。Qdrant 根据可用索引、条件的复杂性以及过滤结果的基数选择一种查询执行选项。此过程称为查询规划。
策略选择过程严重依赖于启发式方法,并且可能因版本而异。然而,一般原则是
- 规划是针对每个 segment 独立执行的(有关 segment 的更多信息,请参阅存储)
- 如果点数低于阈值,则优先进行完全扫描
- 在选择策略之前估算过滤结果的基数
- 如果基数低于阈值,则使用 payload 索引检索点(参见索引)
- 如果基数高于阈值,则使用可过滤向量索引
您可以使用配置文件以及为每个集合单独调整阈值。
